Advanced - Valve Development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Template:Cardiac_modules}} | {{Template:Cardiac_modules}} | ||
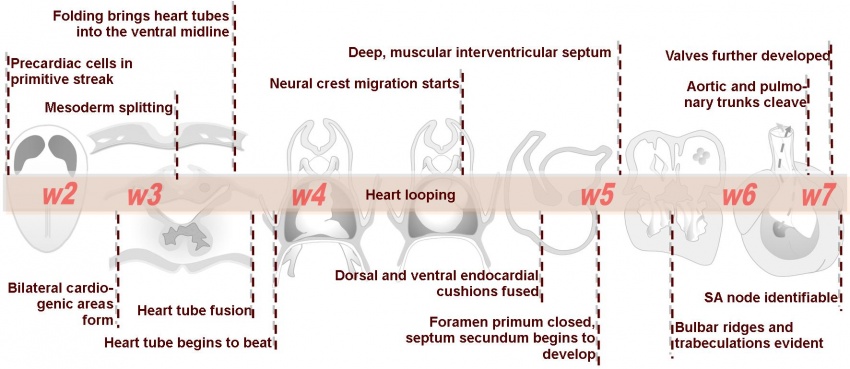
[[Image: | [[Image:Advanced Heart Development Timeline.jpg|center|850px]] | ||
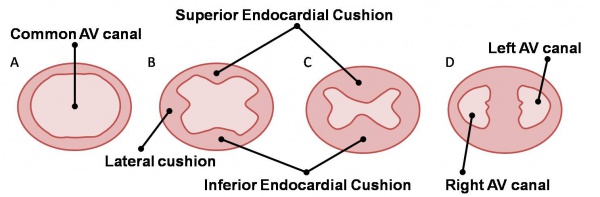
[[Image: | [[Image:AV Canal Division (Superior View).jpg|thumb|right|upright=2]][[Image:AV Valves.jpg|thumb|right|upright=2|Development of the mitral and tricuspid valves]]Many of the mechanisms involved in the development of cardiac valves, particularly the process of epithelial to mesenchymal transformation (EMT), are poorly understood. Much of valve formation revolves around expansion of endocardial cushion tissue, yet limitation of cell proliferation is vital in ensuring the cushion swellings can be remodelled to form thin sheets. EMT, which allows for cushion proliferation, is limited by neurofibromin acting through the inhibition of Ras signalling as well as Smad6 which interferes with TGFβ signalling. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Semilunar Valves.jpg|thumb|left|upright=2|Development of the semilunar valves]] | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Semilunar Cusps.jpg|thumb|left|upright=2|Development of the semilunar cusps]] | ||
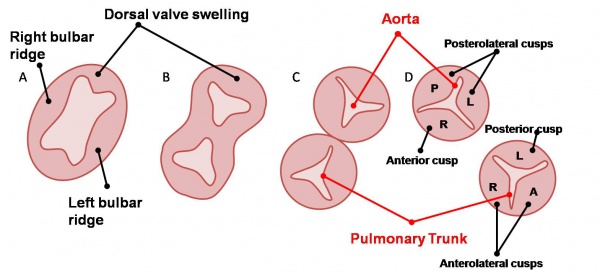
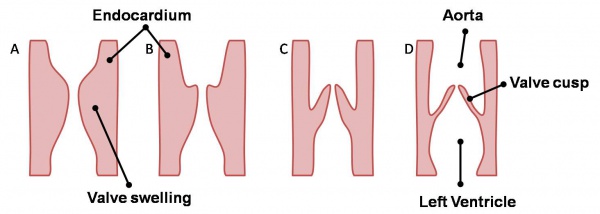
The aortic and pulmonary valves, termed the semilunar valves, are formed from the bulbar ridges and subendocardial valve tissue. The primordial semilunar valve consists of a mesenchymal core covered by endocardium. Excavation occurs, thinning the valve tissue thus creating its final shape (see left). These valves form the four valves of the adult heart depicted below. The mechanisms of valve remodelling in these final steps in both the AV and semilunar valves are not fully understood yet are thought to involve apoptotic pathways. | The aortic and pulmonary valves, termed the semilunar valves, are formed from the bulbar ridges and subendocardial valve tissue. The primordial semilunar valve consists of a mesenchymal core covered by endocardium. Excavation occurs, thinning the valve tissue thus creating its final shape (see left). These valves form the four valves of the adult heart depicted below. The mechanisms of valve remodelling in these final steps in both the AV and semilunar valves are not fully understood yet are thought to involve apoptotic pathways. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{| width="100%" | {| width="100%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|width="30%" bgcolor=" | |width="30%" bgcolor="#FF6666"|<big>'''[[Advanced_-_Outflow_Tract|Back to Outflow Tract]]'''</big> | ||
| | | | ||
|width="30%" bgcolor=" | |width="30%" bgcolor="#FF6666" align="right"|<big>'''[[Advanced_-_Cardiac_Conduction|Next: Conduction System]]'''</big> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|bgcolor="gold"|<big>'''[[Intermediate_-_Heart_Valves|Go to this section in the intermediate level]]'''</big> | |bgcolor="gold"|<big>'''[[Intermediate_-_Heart_Valves|Go to this section in the intermediate level]]'''</big> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 14 March 2010
| Begin Advanced | Heart Fields | Heart Tubes | Cardiac Looping | Cardiac Septation | Outflow Tract | Valve Development | Cardiac Conduction | Cardiac Abnormalities | Molecular Development |
| Cardiac Embryology | Begin Basic | Begin Intermediate | Begin Advanced |
Many of the mechanisms involved in the development of cardiac valves, particularly the process of epithelial to mesenchymal transformation (EMT), are poorly understood. Much of valve formation revolves around expansion of endocardial cushion tissue, yet limitation of cell proliferation is vital in ensuring the cushion swellings can be remodelled to form thin sheets. EMT, which allows for cushion proliferation, is limited by neurofibromin acting through the inhibition of Ras signalling as well as Smad6 which interferes with TGFβ signalling.
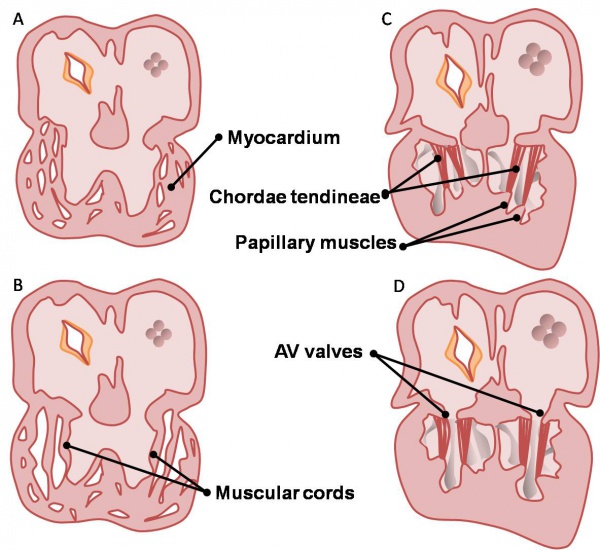
The AV valves begin to form between the fifth and eighth weeks of development. The valve leaflets are attached to the ventricular walls by thin fibrous chords: the chordae tendineae, which insert into small muscles attached to the ventricle wall: the papillary muscles. These structures are sculpted from the ventricular wall. The left AV valve has anterior and posterior leaflets and is termed the bicuspid or mitral valve. The right AV valve has a third, small septal cusp and thus is called the tricuspid valve. These concepts are depicted on the right.
The aortic and pulmonary valves, termed the semilunar valves, are formed from the bulbar ridges and subendocardial valve tissue. The primordial semilunar valve consists of a mesenchymal core covered by endocardium. Excavation occurs, thinning the valve tissue thus creating its final shape (see left). These valves form the four valves of the adult heart depicted below. The mechanisms of valve remodelling in these final steps in both the AV and semilunar valves are not fully understood yet are thought to involve apoptotic pathways.
| Back to Outflow Tract | Next: Conduction System | |
| Go to this section in the intermediate level |