ANAT2341 Lab 10 - Fetal
| 2011 Lab 10: Introduction | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Hearing
- Week 9 - Mesenchyme surrounding membranous labryinth (otic capsule) chondrifies. (More? Human 10 Week Fetus)
- Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labryinth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph.
- Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
- 3rd Trimester - Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle response in fetus.
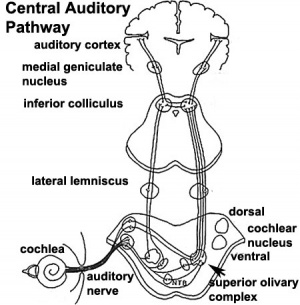
Central Pathway
- 26 weeks - human brainstem auditory pathway is anatomically formed.
- 28 weeks - Automated Auditory Brainstem Response ( AABR) can be recorded.
less than 34 weeks - latencies of AABR components (I, III, and V) decrease as a function of gestation
Fetal Neural
Timeline of events in Human Neural Development
|
|
|
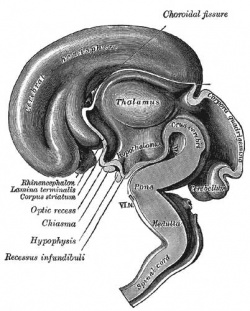
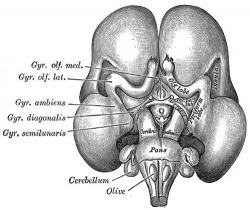
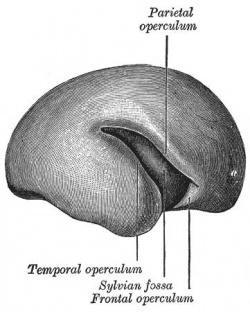
| Human brain at three months (median sagittal section) | Human brain at four months (inferior surface) | Human brain at five months (outer surface) |
During the fetal period there is ongoing growth in size, weight and surface area of the brain and spinal cord. Microscopically there is ongoing: cell migration, extension of processes, cell death and glial cell development.
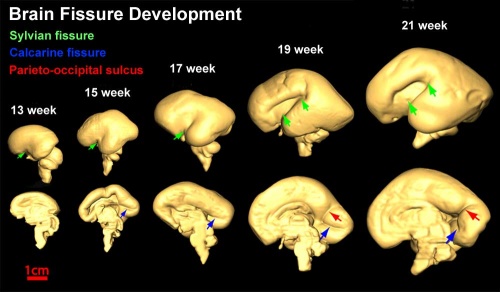
Cortical maturation (sulcation and gyration) and vascularization of the lateral surface of the brain starts with the insular cortex (insula, insulary cortex or insular lobe) region during the fetal period. This cerebral cortex region in the adult brain lies deep within the lateral sulcus between the temporal lobe and the parietal lobe.
- sulcation - The process of brain growth in the second to third trimester which forms sulci, grooves or folds visible on fetal brain surface as gyri grow (gyration). Abnormalities of these processes can lead to a smooth brain (lissencephaly).
- gyration - The development of surface folds on the brain (singular, gyrus)
Insular Gyral and Sulcal Development
- 13-17 gestational weeks - appearance of the first sulcus
- 18-19 gestational weeks - development of the periinsular sulci
- 20-22 gestational weeks - central sulci and opercularization of the insula
- 24-26 gestational weeks - covering of the posterior insula
- 27-28 gestational weeks - closure of the laeteral sulcus (Sylvian fissure or lateral fissure)
(Data from[1])
- Between 29-41 weeks volumes of: total brain, cerebral gray matter, unmyelinated white matter, myelinated, and cerebrospinal fluid (from MRI)
- grey matter- mainly neuronal cell bodies; white matter- mainly neural processes and glia.
- total brain tissue volume increased linearly over this period at a rate of 22 ml/week.
- Total grey matter also showed a linear increase in relative intracranial volume of approximately 1.4% or 15 ml/week.
- The rapid increase in total grey matter is mainly due to a fourfold increase in cortical grey matter.
- Quantification of extracerebral and intraventricular CSF was found to change only minimally.
(Text - modified from [2])
Neural development will continue after birth with substantial glial development, growth, death and reorganization occuring during the postnatally.
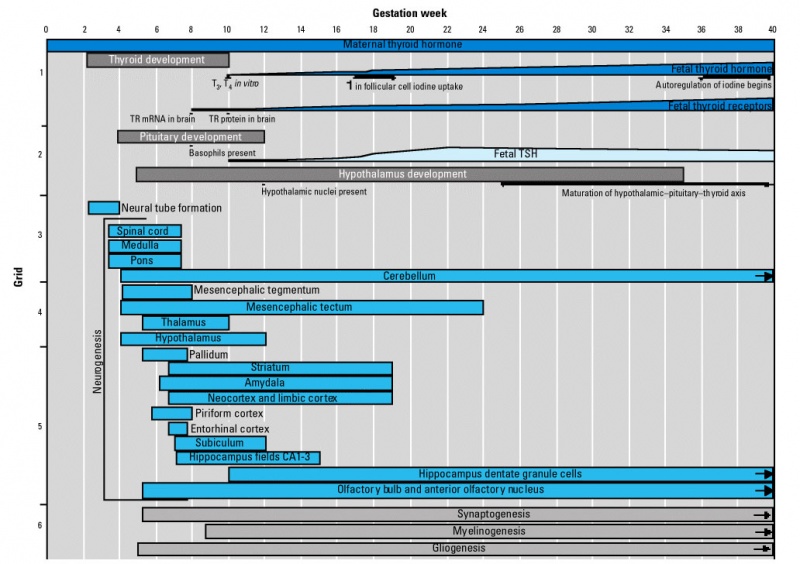
Thyroid System and Neural Development
Timeline of human thyroid system and brain development from conception to birth.[3] (Estimation of neurogenesis adapted from Bayer et al.[4])
References
| 2011 Lab 10: Introduction | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology ANAT2341 Lab 10 - Fetal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2341_Lab_10_-_Fetal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G