ANAT2241 Female Reproductive System
| ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the virtual science practical class and provides additional information for student self-directed learning purposes. All practical class pages are located on Moodle - ANAT2241 |
General Objective
To know the histological and cytological structure of the major organs of the female reproductive system.
Specific Objectives
- To describe the microanatomy of the ovary and to identify: peritoneal mesothelium, developing ovarian follicles, Graafian and atretic follicles.
- To know the layers of the wall of the uterine tube (Fallopian tube or oviduct).
- To know the structure of the uterus and the morphological changes of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle.
- To know the structure of the mammary glands.
Learning Activities
Examine the following virtual slides, and in course manual identify, draw and label the structures listed and note the function.
ANAT2241 Virtual Slides: ANAT2241 Female Reproductive
Uterine Tube
(oviduct, fallopian tube)
- uterine tube acts as a conduit for the oocyte, from the ovaries to the uterus.
- consists of a mucosa and a muscularis.
- peritoneal surface of the oviduct is lined by a serosa and subjacent connective tissue.
Mucosa
- ciliated and secretory epithelium resting on a cellular lamina propria.
- number of ciliated cells and secretory cells varies along the tube.
- secretory activity varies during the menstrual cycle, and resting secretory cells are also referred to as peg-cells. Some of the secreted substances are thought to nourish the oocyte and the very early embryo.
Muscularis
- inner circular muscle layer and an outer longitudinal layer.
- inner longitudinal layer is present in the isthmus and the intramural part.
- peristaltic muscle action for the transport of spermatozoa and oocyte.
Parts
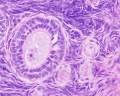
- infundibulum - funnel-shaped (up to 10 mm in diameter) end of the oviduct. Finger-like extensions of its margins, the fimbriae, are closely applied to the ovary. Ciliated cells are frequent.
- ampulla - mucosal folds, or plicae, and secondary folds which arise from the plicae divide the lumen of the ampulla into a very complex shape. Fertilization usually takes place in the ampulla.
- isthmus - narrowest portion (2-3 mm in diameter) of the tube located in the peritoneal cavity. Mucosal folds are less complex and the muscularis is thick. An inner, longitudinal layer of muscle is present in the isthmus.
- intramural part - penetrates the wall of the uterus.
The mucosa is smooth, and the inner diameter of the duct is very small.
Histology
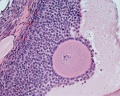
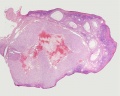
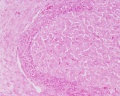
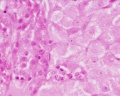
Ovary Histology
Ovary histology: Tunica Albuginea x20 | Tunica albuginea, Germinal epithelium x40 |
Primary follicle, primordial follicle, oocyte, x40 | Secondary follicle, cumulus oophorus, zona pelucida, granulosa cells, oocyte x20 | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, Loupe | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, x10 | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, x40 | Corpus albicans, primary follicle, primordial follicle, granulosa cells, oocyte x20 | Menstrual Cycle | Ovary Development
Menstrual Histology
Menstrual Cycle - Histology (images are listed in sequence and uterine endometrium from dilatation and curettage)
- Uterine Endometrium: menstrual | mid-proliferative | late proliferative | secretory | late secretory
- Vaginal Smear: early proliferative | mid-proliferative | late proliferative | secretory | late secretory
Links: Menstrual Cycle - Histology | Menstrual Cycle | Papanicolaou stain
Course Links
- Histology Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ANAT2241 Support | Histology | Histology Stains | Embryology Glossary
| Common Histology Stains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Practical Support
- Pages can be accessed from any internet connected computer.
ANAT2241 Support Links: The Virtual Microscope | Covering and Lining Epithelia | Glandular Epithelia | CT Components | CT Types | Bone, Bone Formation and Joints | Muscle | Nervous | Blood | Eye | Cardiovascular | Respiratory | Integumentary | Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal Organs | Lymphatic and Immune | Endocrine | Urinary | Female Reproductive | Male Reproductive | Histology Stains | Histology Drawings | Practicals Health and Safety 2013 | Moodle - 2019
ANAT2241 This practical support page content is not part of the science practical class and provides only background information for student self-directed learning purposes.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology ANAT2241 Female Reproductive System. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/ANAT2241_Female_Reproductive_System
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G