2017 Group Project 3
| 2017 Student Projects | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Help:Copyright Tutorial Help:Editing Basics
Heart
Mark Hill (talk) 16:06, 14 September 2017 (AEST) OK Feedback
- This is very early stage of content development. Of all the possible topics this is definitely the MOST researched topic to date. You have this week to make significant progress on this page.
- Where is the timeline of development.
- Where is the timeline of key discoveries
- Splanchnic mesoderm and neural crest contribution
- Differentiation of different cardiac cell types
- Cardiac conduction system development
- Cardiomyocyte differentiation/function
- Cardiac stem cells
Introduction
The cardiovascular system is the first system to develop and function in the human embryo. The rapid cardiac development is essential as the growing embryo can no longer receive oxygen and essential nutrients via diffusion alone, hence a circulatory system and a contractile heart mechanism is required to supply the embryo. We recognise the hearts normal development is vital for foetal life, and hence we have chosen to document the development of the heart from gastrulation to birth. Any defects occurring during the developmental processes can lead to congenital heart abnormalities. However, early cardiac development is a multifaceted procedure and is associated with other developmental processes such as: embryonic folding, coelom formation, and vascular development [1].
Through researching the advances in technology, coupled with the biological use of suitable animal models [2] our understanding of embryological cardiac development has evolved, and we are piecing together the mechanism underlying this development. This page will outline the importance of how heart abnormalities arise, the treatments available and the possible treatments to be developed in the future. Due to the major knowledge gaps in current embryological heart research, we acknowledge that this will impact our assignment, and aim to address further research concepts that will improve our understanding
<pubmed> PMC1767747</pubmed>
z5076019
Developmental Origin
PubMed Searches:
[3] <pubmed>PMC1767747</pubmed>
Z5076019 (talk) 14:19, 26 August 2017
Developmental Timeline
Embryonic Developmental Timeline
week 4-5 - precardiac cells in primitive streak, bilateral cardiogenic areas form, mesoderm splitting, heart tube fusion week 6-7 - neural crest migration starts, dorsal and ventral endocardial cushions fused, foramen closes, septum secundum begins to develop week 8-9 - bulbular ridges and trabeculations evident, aortic and pulmonary trunks cleave, valves furthur developed, SA node identifiable
Historic Developmental Timeline
z5178463
Developmental Signalling Processes
Heart development is a very complicated and dynamic process that requires a high degree of control and regulation. This control is achieved by different molecular pathways expressed at different stages of heart development.
Wnt signalling
Both canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways have a role in different stages of cardiac development. These two pathways may have an overlapping role in in cardiac development or they may work independent. The canonical Wnt signalling pathway involves β-catenin and is activated by a number of ligands such as Wnt-1, Wnt-2, Wnt-3A, Wnt-8A, Wnt-8B, Wnt-8C, Wnt-10A, and Wnt-10B. However, the non-canonical signalling pathway is associated with planar cell polarity and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways that are activated by different ligands such as Wnt4, Wnt5A, Wnt5B, Wnt6, Wnt7A, Wnt7B, and Wnt11 [1].
Transforming growth factor β
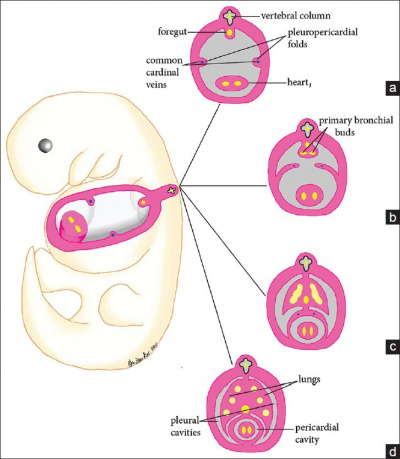
Mark Hill (talk) 15:57, 31 August 2017 (AEST) OK this image requires a better descriptive name than "Fig2.jpg"
Z5076466
Current Research And Findings
- all
[|The Role of Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger 1 in Maintaining Ductus Arteriosus Patency]
Z5018962 (talk)z5018962Z5018962 (talk)
Animal Models
z5076466
Abnormal Development
Ventricular Septal Defect
[13] - ventricular septal defect (Penny and Vick)
Atrial Septal Defect
[14] - atrial septal defects (Giva, Martins & Wald)
Atrioventricular Septal Defect
Misc. References
z5059996
Future Questions
Z5076466
Glossary of Terms
- all
References
- all