2011 Lab 6 - Fetal
| 2011 Lab 6: Introduction | Trilaminar Embryo | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Fetal Growth
|
<Flowplayer height="320" width="285" autoplay="true">fetal growth.flv</Flowplayer> |
In this cartoon movie of fetal growth, observe the changing relative sizes of the head and body.
|
Skull Ossification
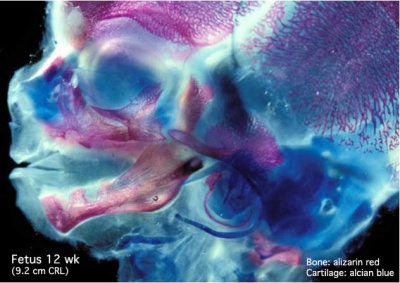
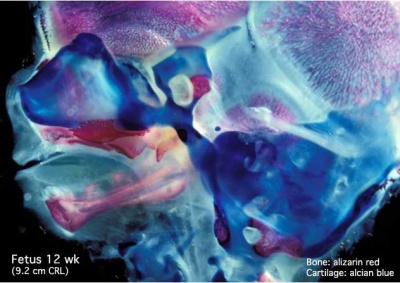
These are 2 views of the same 12 week 92 mm CRL human fetus head, double stained to show both cartilage (blue) and newly-formed bone (red). The head undergoes two different forms of ossification (endochondral and intramembranous) in separate regions of the skull.
In this lateral (external) view, note the distribution of new bone formation by intramembranous ossification in the plates of the cranial vault, temporal bone, orbit, upper jaw (maxilla) and lower jaw (mandible) regions. (More? Skull | Face) Bony regions in the lower jaw (mandible) region also show spaces where tooth formation is occuring.
In this medial (internal) view, note the distribution of cartilage from the nasal region through the base of the skull showing endochondral ossification, also occuring in the atlas/axis (with new bone forming). See also the original Meckel's cartilage within the newly forming bony mandible.
Face
The cartilage template of the mandible and the base of the skull are replaced by early bone development.
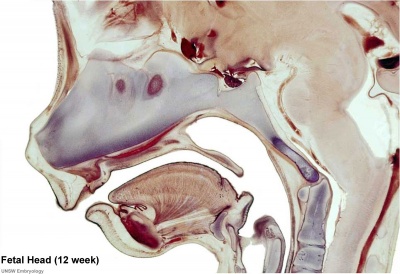
Selected midline medial head view showing key features of head musculoskeletal and neurological development.
Note extensive nasal cartilage, nasal conchae, pituitary, secondary palate, oral cavity, tongue, mandible, hyoid, choana, oropharynx.
Also note the developing tongue musculature and its mandibular attachment site.
Note that the cranial vault, the portion of the skull enclosing the brain, ossifies by a unique bone formation process, intramembranous ossification.
Because the head contains many different structures also review notes on Special Senses (eye, ear, nose), Respiration (pharynx), Integumentary (Teeth), Endocrine (thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary) and Musculoskeletal (tongue, skull).
Palate Development
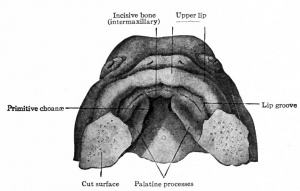
|
||
| Embryonic Palate (week 7) | Quicktime | Flash | Quicktime | Flash |
Hearing
- Week 9 - Mesenchyme surrounding membranous labryinth (otic capsule) chondrifies. (More? Human 10 Week Fetus)
- Week 12-16 - Capsule adjacent to membranous labryinth undegoes vacuolization to form a cavity (perilymphatic space) around membranous labrynth and fills with perilymph.
- Week 16-24 - Centres of ossification appear in remaining cartilage of otic capsule form petrous portion of temporal bone. Continues to ossify to form mastoid process of temporal bone.
- 3rd Trimester - Vibration acoustically of maternal abdominal wall induces startle response in fetus.
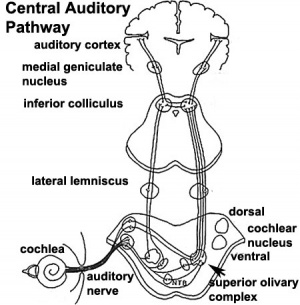
Central Pathway
- 26 weeks - human brainstem auditory pathway is anatomically formed.
- 28 weeks - AABR can be recorded.
less than 34 weeks - latencies of AABR components (I, III, and V) decrease as a function of gestation