2011 Lab 3 - Week 4
| 2011 Lab 3: Introduction | Week 3 | Week 4 | Abnormalities | Online Assessment | Group Project |
Week 4
Key Events of Human Development during the fourth week (week 4) following fertilization or Clinical week 6 (LMP).
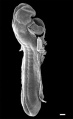
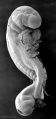
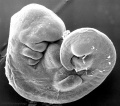
These notes cover the fourth week of embryonic development, which is the beginning of organogenesis, (specific tissues and systems are beginning to differentiate) from the trilaminar embryo. With many parallel processes, descriptions begin to get complicated! Many of the described processes begin and extend over a broader range of time. Some developmental processes will be discussed later in the practical to simplify matters.
Ectoderm on the embryo surface undergoes segmentation: The central portion of the embryonic disc forms the neural plate, the edge of this plate forms neural crest and the remainder outside this forms the epitheium of the skin and other structures.
Neurogenesis
- Central Nervous System (CNS) - the neural plate undergoes morphological changes to form the primitive central nervous system (brain, spinal cord). An epithelial layer of cells which contributes all neural (brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system) and the external epithelium (surface layer of the skin) of the embryo. Neurogenesis begins towards the end of week 3, when the neural tissues separate from this germ cell layer.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - the neural crest cells in the body region migrate and spread to different regions of the embryo forming the PNS (dorsal root ganglia, sympathetic ganglia, enteric nervous system) and many other embryonic tissues. Neural crest cells in the head region form skeletal and other structures.
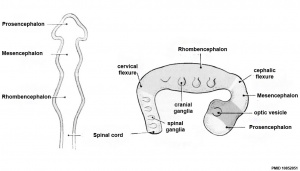
Pharyngeal Arches
In the head region, a series of ventral folds form under the brain in a rostral to caudal sequence, these are the pharyngeal arches.
Placodes
In the head region, ectoderm small patches form pairs of specialised placodes that eventually contribute to specific sensory components, cranial ganglia and the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis).
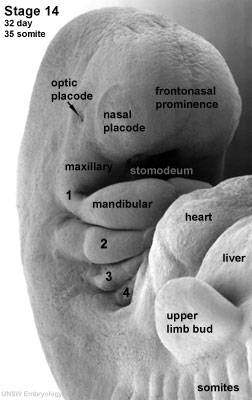
Limb Buds
In the body region, limb buds form initially as ectoderm and mesoderm (somitic and somatic) components and are the "paddle-like" projections from the trunk which will form all the upper and lower limb components. (An overview of limb development will be covered in week 8).
Cardiogenesis
Within the embryo mesoderm, the heart tube and vascular development continues. Cardiogenesis will be covered in week 5, when septation begins.
Neurogenesis
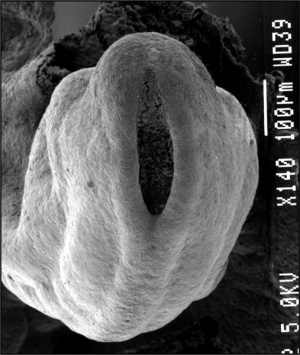
Developmental sequence: neural plate -> (day 18-19) neural groove -> neural tube -> Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) - the neural plate undergoes morphological changes to form the primitive central nervous system. An epithelial layer of cells which contributes all neural (brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system) and the external epithelium (surface layer of the skin) of the embryo. Neurogenesis begins towards the end of week 3, when the neural tissues separate from this germ cell layer.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - the neural crest cells in the body region migrate and spread to different regions of the embryo forming the PNS and many other embryonic tissues. Neural crest cells in the head region form skeletal and other structures.
Human Neuralation - Early Stages
The stages below refer to specific Carneigie stages of development.
- stage 8 (about 18 postovulatory days) neural groove and folds are first seen
- stage 9 the three main divisions of the brain, which are not cerebral vesicles, can be distinguished while the neural groove is still completely open
- stage 10 (two days later) neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when neural crest cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm
- stage 11 (about 24 days) the cranial neuropore (rostral, cephalic or anterior) closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in several areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently.
- stage 12 (about 26 days) The caudal (posterior) neuropore takes a day to close
- the level of final closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31
- corresponds to the level of sacral vertebra 2
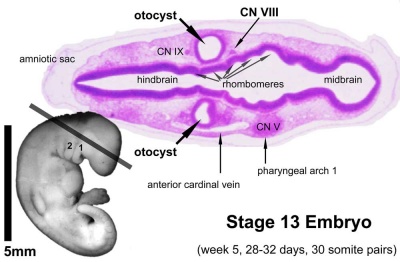
- stage 13 (4 weeks) the neural tube is normally completely closed.
Three primary brain vesicles develop initially due to the neural plate being broader at the cranial (brain) end than the narrower caudal (spinal cord) end. When the plate fuses to form a tube, these 3 initial expansions (vesicles) result.
Pharyngeal Arches and Placodes
In the head region, two main components of head development form the pharyngeal arches and sensory placodes.
- Pharyngeal arches form a series of ventral folds under the brain in a rostral to caudal sequence. These arches will form most of the head and neck structures of the embryo and contain all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm). The topic of head and sensory development is covered in detail in BGD cycle B.
- Small patches of ectoderm form pairs of specialised placodes that eventually contribute to specific sensory components, cranial ganglia and the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis).
Embryo Stage 13
Movies - Embryo Carnegie stage 13 - These are rotating animations based upon reconstruction of individual serial slice images of the stage 13 embryo.
| Central Nervous System | Gastrointestinal | Cardiovascular |
Week 4 Movies
Note that many of the movies start in week 4 and continue on through later embryonic development.
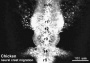
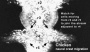
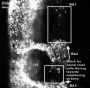
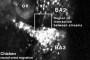
Ectoderm
| Neural Plate | Neural Tube |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Mesoderm
| Mesoderm | Somite Structures | Vertebra |
Endoderm
| 2011 Lab 3: Introduction | Week 3 | Week 4 | Abnormalities | Online Assessment | Group Project |