2010 Lecture 12: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Neural Crest Development= | |||
== Introduction == | |||
The neural crest are bilaterally paired strips of cells arising in the ectoderm at the margins of the neural tube. These cells migrate to many different locations and differentiate into many cell types within the embryo. This means that many different systems (neural, skin, teeth, head, face, heart, endocrine, gastrointestinal tract) will also have a contribution fron the neural crest cells. | |||
In the body region, neural crest cells also contribute the peripheral nervous system (both neurons and glia) consisting of sensory ganglia (dorsal root ganglia), sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia and neural plexuses within specific tissues/organs. | |||
In the head region, neural crest cells migrate into the pharyngeal arches (as shown in movie below) forming '''ectomesenchyme''' contributing tissues which in the body region are typically derived from mesoderm (cartilage, bone, and connective tissue). General neural development is also covered in Neural Notes. | |||
==Lecture Objectives== | |||
[[File:Carnegie stage 13 caudal trunk.jpg|thumb|Human Embryo (Carnegie stage 13) caudal trunk<ref><pubmed>18689800</pubmed>| [http://hmg.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/17/21/3411 Hum Mol Genet.]</ref>]] | |||
* Understand the structures derived from ectoderm. | |||
* Understand the formation of neural folds. | |||
* Identify the initial location of neural crest cells in the trilaminar embryo. | |||
* Identify pathways of neural crest migration throughout the embryo. | |||
* To know the major tissues to which neural crest cells contribute. | |||
* To know how abnormalities in development that result from abnormal neural crest cell migration. | |||
* Understand how neural crest cells contribute to the pharyngeal arches and the head structures they form. | |||
== Textbook References == | |||
* '''The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology''' (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 4 p61-63 - p71,75, 385, 392 p393-94 (figure showing cell types); Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240, | |||
* '''Larsen’s Human Embryology''' by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 4 p74-82 - Chapter 5, experimental methods; Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418 | |||
* [[Neural Crest Development]] | |||
==Neural Crest Migration in the Head== | |||
{| border='0px' | |||
|- | |||
| <Flowplayer width="408" height="320" autoplay="true">Chicken-neural crest migration 01.flv</Flowplayer> | |||
| valign="top" |[[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-01.jpg|300px]] | |||
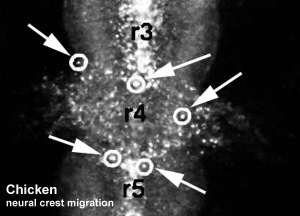
Chicken embryo sequence shows the migration of DiI-labeled neural crest cells towards the branchial arches as the embryo. | |||
White rings indicate migration of individual cells. Each image represents 10 confocal sections separated by 10 microns. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Movie Source: Original Neural Crest movies kindly provided by Paul Kulesa. | |||
'''Related Movies:''' [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 01|Migration 01]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 02|Migration 02]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 03|Migration 03]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 04|Migration 04]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 05|Migration 05]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 06|Migration 06]] | [[Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 07|Migration 07]] | |||
==Early Development and Neural Derivatives== | |||
[[File:Neuralplate cartoon.png|right]] | |||
* bilaminar embryo- hypoblast | |||
* trilaminar embryo - ectoderm layer | |||
** neural plate - neural groove - neural tube and neural crest | |||
* cranial expansion of neural tube - central nervous system | |||
* caudal remainder of neural tube - spinal cord | |||
Neural Crest - contributes both neural and non-neural cells | |||
* dorsal root ganglia | |||
* parasympathetic / sympathetic ganglia. | |||
==Neural Crest Origin== | |||
* lateral region of neural plate | |||
* dorsal neural fold->tube | |||
Two main embryo regions | |||
* Head (CNS) - differentiate slightly earlier, mesencephalic region of neural folds | |||
* Body (spinal cord) - lateral edges of fused neural tube | |||
== Neural Crest Generation == | |||
* cranial region - Begins when still neural fold | |||
* spinal cord - from day 22 until day 26 | |||
** after closure of caudal neuropore | |||
** rostro-caudal gradient of differentiation | |||
Studies using the chicken model demonstrated that they are not a segregated population. Interactions between the neural plate and epidermis can generate neural crest cells, since juxtaposition of these tissues at early stages results in the formation of neural crest cells at the interface. | |||
At cranial levels, neuroepithelial cells can regulate to generate neural crest cells when the endogenous neural folds are removed, probably via interaction of the remaining neural tube with the epidermis. | |||
Progenitor cells in the neural folds are multipotent, having the ability to form multiple ectodermal derivatives, including epidermal, neural crest, and neural tube cells the neural crest is an induced population that arises by interactions between the neural plate and the epidermis. | |||
The competence of the neural plate to respond to inductive interactions changes as a function of embryonic age. | |||
(Text from: Bronner-Fraser M PNAS 1996 Sep 3;93(18):9352-7) | |||
== Neural Crest Derivatives == | |||
Neural crest progenitor cells migrate throughout the embryo and give rise to many different adult cells. | |||
This Includes: ganglia cranial, dorsal root, sympathetic trunk, celiac, renal, plexus in GIT, glia, schwann cells, melanocytes (skin), and adrenal medulla (chromaffin cells). | |||
In the head region neural crest also gives rise to a number of connective tissue structures. | |||
===Neural Crest - Head=== | |||
(see also [[2009_Lecture_11|Head Development Notes]]) | |||
Mesencephalon and caudal Proencephalon | |||
* parasympathetic ganglia CN III | |||
* connective tissue around eye and nerve | |||
* head mesenchyme | |||
* pia and arachnoid mater | |||
* dura from mesoderm | |||
Mesencephalon and Rhombencephalon | |||
* pharayngeal arches | |||
* look at practical notes on neck and head. | |||
* cartilage rudiments (nose, face, middle ear) | |||
* face | |||
* dermis, smooth muscle and fat | |||
* odontoblasts of developing teeth | |||
Rhombencephalon | |||
* C cells of thyroid | |||
* cranial nerve ganglia | |||
* neurons and glia | |||
* parasympathetic of VII, IX, X | |||
* sensory ganglia of V, VII, VIII, IX, X | |||
===Neural Crest- Spinal Cord=== | |||
* peripheral nervous system | |||
* dorsal root ganglia (sensory N) | |||
* parasympathetic ganglia | |||
* sympathetic ganglia | |||
* motoneurons in both ganglia | |||
* all associated glia | |||
== Neural Crest Migration == | |||
===Head=== | |||
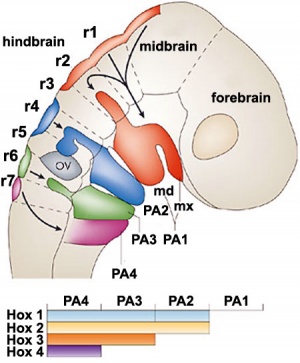
[[File:Hindbrain neural crest migration.jpg|thumb|Hindbrain neural crest migration]] | |||
{| border='0px' | |||
|+ '''Neural crest migration in the head in chicken''' ([[Movies_-_Chicken_Neural_Crest|chicken neural crest movies overview]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-01.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 01]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-02.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 02]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-03.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 03]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-04.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 04]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-05.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 05]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-06.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 06]] | |||
| [[File:Chicken-neural-crest-migration-07.jpg|90px|link=Movie - Chicken Neural Crest Migration 07]] | |||
|} | |||
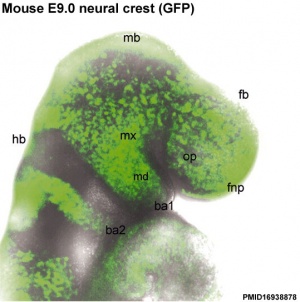
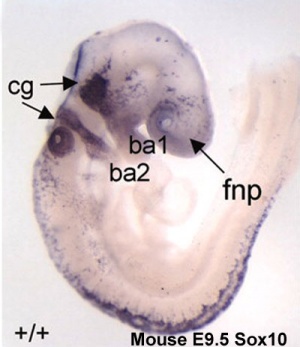
[[File:Mouse_head_E9-neural_crest_GFP.jpg|300px||Mouse_head_E9-neural_crest_GFP]] [[File:Hindbrain neural crest migration.jpg|300px|Hindbrain neural crest migration]] [[File:Mouse-E9.5-Sox10.jpg|300px|Mouse-E9.5-Sox10.jpg]] | |||
===Trunk=== | |||
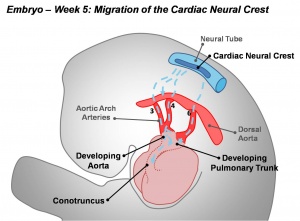
===Cardiac Outflow Tract=== | |||
[[File:Cardiac_Neural_Crest_Migration.jpg|300px]] | |||
[[File:Human neural crest cell migration-in vitro.jpg|thumb|Human neural crest cell migration (in vitro)<ref><pubmed>18689800</pubmed>| [http://hmg.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/17/21/3411 Hum Mol Genet.]</ref>]] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3118 Figure 13.2. Neural crest cell migration in the trunk of the chick embryo] | |||
* Neural crest at the level of the body have two general migration pathways, defined by the position of the somite | |||
** medial pathway - between the neural tube and the somite | |||
** lateral pathway - between the somite and the body wall | |||
[[File:Trunk neural crest migration.jpg|thumb|Trunk neural crest migration]] | |||
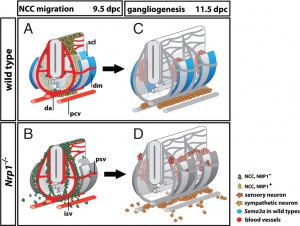
* A recent study of guidance of neural crest cells (NCC) in mice show migrate 3 specific pathways. | |||
** SEMA3A and its receptor neuropilin 1 (NRP1) - act as repulsive guidance cues | |||
** migration pathway did not affect specification - differs from the concept of migration pathway specifying the neural crest cell differentiation pathway | |||
Neural crest at the level of the head have a different migration pathway. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3134 Figure 13.7. Cranial neural crest cell migration in the mammalian head] | |||
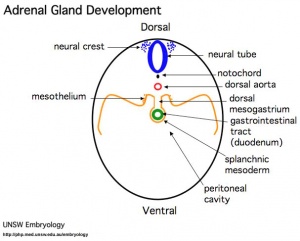
===Sympathetic Ganglia and Adrenal Medulla=== | |||
[[File:Adrenal_medulla.jpg|300px]] | |||
[[Media:Adrenal_medulla.mov]] | |||
===Enteric nervous system=== | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=eurekah&part=A63004&rendertype=figure&id=A63009 Figure 1. Diagram of an E10 embryo showing the origins of neural crest cells that colonize the developing gastrointestinal tract] | |||
==Historic Migration Experiments== | |||
Key early experiments in understanding the pattern of neural crest migration were carried out by [[Embryology_History_-_Nicole_Le_Douarin|LeDouarin]] in the 1980's (see Development of the peripheral Nervous system from the neural crest, Ann Rev Cell Biol 4 p375) | |||
[http://www.sdbonline.org/archive/dbcinema/ledouarin/ledouarin.html Quail-Chick Chimeras] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.63 Figure 1.11. Neural crest cell migration Chimera experiment] | |||
These transplantation studies in chicken/quail chimeras utilised the different nucleoli appearance of cells to differentiate different species. Thus transplanation and subsequent histological processing allowed identification of the migration path and final destination of transplanted neural crest cells. | |||
Similar later experiments have now been carried out using the neural crest cells molecularly tagged with (LacZ). | |||
==Abnormalities== | |||
===Neuroblastoma=== | |||
[[File:Neuroblastoma.jpg|thumb|Neuroblastoma]] | |||
[[File:Childhood cancer survival rates.jpg|thumb|Childhood cancer survival rates]] | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/256700 OMIM - Neuroblastoma] | |||
===Digeorge Syndrome (DGS)=== | |||
[[File:Digeorge chromosome22.jpg|thumb|Digeorge chromosome 22]] | |||
* DiGeorge syndrome is the most frequent microdeletion syndrome in humans caused by a hemizygous deletion (1.5 to 3.0-Mb) of chromosome 22q11.2. | |||
* Velo-cardio-facial syndrome, Hypoplasia of thymus and parathyroids, third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome. | |||
* Abnormalities: cardiovascular, thymic and parathyroid, craniofacial anomalies, renal anomalies, hypocalcemia and immunodeficiency. | |||
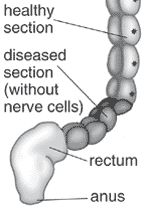
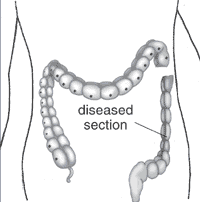
===Intestinal Aganglionosis=== | |||
[[File:Megacolon surgery.gif]] | |||
[[File:Megacolon stoma.gif]] | |||
* Intestinal Aganglionosis, Hirschsprung's Disease or Megacolon | |||
* lack of enteric nervous system (neural ganglia) in the intestinal tract responsible for gastric motility (peristalsis). | |||
* severity is dependent upon the amount of the GIT that lacks intrinsic ganglia, due to developmental lack of neural crest migration into those segments. | |||
* first indication in newborns is an absence of the first bowel movement, other symptoms include throwing up and intestinal infections. | |||
* Clinically this is detected by one or more tests (barium enema and x ray, manometry or biopsy) and can currently only be treated by surgery. A temoporary ostomy (Colostomy or Ileostomy) with a stoma is carried out prior to a more permanent pull-through surgery. | |||
===Melanoma=== | |||
[[File:Melanoma.jpg]] | |||
* In Australia each year 8,800 people are diagnosed with melanoma, and almost 1000 people die (Data, Cancer Council Australia). | |||
* Two different findings on the reprogramming of melanoma cells, which have a neural crest origin, when transplanted between species into embryos. | |||
[http://www.melanoma.com/staging.html Melanoma staging] | |||
===Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)=== | |||
* Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (von Recklinghausen) occurs in 1 in 3,000 to 4,000 people with characteristic skin blemishes forming in early childhood. | |||
* Multiple ''café-au-lait'' spots (flat skin patches darker than the surrounding area) appear in early childhood which increase in both size and number with age. | |||
* tumors can develop along nerves in the skin, brain, and other parts of the body. In the iris of the eye, Lisch nodules (benign growths) also appear | |||
:(French, ''café-au-lait'' = coffee with milk) | |||
[http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Tumors/NeurofibromaID5098.html Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology- Neurofibroma] | |||
===Tetralogy of Fallot=== | |||
Cardiac abnormality possibly stemming from abnormal [[N#neural crest|neural crest]] migration. Named after Etienne-Louis Arthur Fallot (1888) who described it as "''la maladie blue''". (More? [[Cardiovascular System Development]] | [[Cardiac_Embryology|Cardiac Tutorial]] | [[2009_Lecture_21|Lecture - Heart]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/heart2.htm#Fallot Heart Abnormalities]) | |||
===Treacher Collins syndrome=== | |||
(TCS) A genetic developmental abnormality results from autosomal dominant mutations of the gene TCOF1 encoding the protein Treacle, identified in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8563749 2006]. The syndrome is characterized by hypoplasia of the facial bones, cleft palate, and middle and external ear defects. These defects may relate to the effects on neural crest migration. (More? [[Neural Crest Development]] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/606847 OMIM - TCOF1] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8563749 PMID: 8563749]) | |||
== References == | |||
===Textbooks=== | |||
* '''The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology''' (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240. | |||
* '''Larsen’s Human Embryology''' by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418. | |||
===Online Textbooks=== | |||
* '''Developmental Biology''' by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.section.3109#3133 The Cranial Neural Crest] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3111 Figure 13.1. Regions of the neural crest] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3134 Figure 13.7. Cranial neural crest cell migration in the mammalian head] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3118 Figure 13.2. Neural crest cell migration in the trunk of the chick embryo] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3138 Figure 13.10. Separation of the truncus arteriosus into the pulmonary artery and aorta] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.5460 Figure 22.23. Chick embryo rhombomere neural crest cells and their musculoskeletal packets] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3127 Figure 13.4. Segmental restriction of neural crest cells and motor neurons by the ephrin proteins of the sclerotome] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.43 Figure 1.3. Pharyngeal arches] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.table.3135 Table 13.2. Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches] | |||
:Neural Crest Experiments: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.63 Figure 1.11. Neural crest cell migration Chimera experiment] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=dbio.figgrp.3130 Figure 13.5. Pluripotency of trunk neural crest cells] | |||
* '''Molecular Biology of the Cell''' Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=mboc4.figgrp.3946 Figure 21-80. The main pathways of neural crest cell migration] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=mboc4.figgrp.3968 Figure 21-91. Diagram of a 2-day chick embryo, showing the origins of the nervous system] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=neural_crest&rid=mboc4.figgrp.3511 Figure 19-23. An example of a more complex mechanism by which cells assemble to form a tissue] | |||
* '''Neuroscience''' Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2001[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=neurosci.figgrp.1449 Figure 22.1. Neurulation in the mammalian embryo] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=neurosci.figgrp.1503 Figure 22.12. Cell signaling during the migration of neural crest cells] | |||
* '''Madame Curie Bioscience Database''' Chapters taken from the Madame Curie Bioscience Database (formerly, Eurekah Bioscience Database) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=eurekah&part=A53006 Cranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=eurekah&part=ch2957 Neural Crest Cells and the Community of Plan for Craniofacial Development: Historical Debates and Current Perspectives] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=eurekah&part=A63004&rendertype=figure&id=A63009 Figure 1. Diagram of an E10 embryo showing the origins of neural crest cells that colonize the developing gastrointestinal tract] | |||
* '''Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects''' Siegel, George J.; Agranoff, Bernard W.; Albers, R. Wayne; Fisher, Stephen K.; Uhler, Michael D., editors Philadelphia: Lippincott,Williams & Wilkins; c1999[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?&rid=bnchm.figgrp.1881 Figure 27-10. Neuropoietic model of neural crest cell lineage] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=neural_crest&rid=bnchm.figgrp.1883 Figure 27-11. Growth factor control of neural crest lineage decisions] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=neural_crest&rid=bnchm.figgrp.1893 Figure 27-15. The Schwann cell lineage] | |||
===Search === | |||
* '''Bookshelf''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books&cmd=search&term=neural_crest neural crest] | |||
* '''Pubmed''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/gquery?itool=toolbar&cmd=search&term=neural_crest neural crest] | |||
== UNSW Embryology Links == | |||
* '''Notes:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Introduction] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest2.htm Abnormalities] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest3.htm Stage 13/14] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest4.htm Stage 22] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest5.htm Stage 22 high power] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest6.htm Generation] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest7.htm Migration] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest8.htm Peripheral Ganglia] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest9.htm GIT Enteric] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest12.htm Heart][http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest10.htm Molecular] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncresttxt.htm Text only] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrestlink.htm Web Links] | |||
* '''Lectures:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Science/ANAT2341lecture13.htm ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 13] | |||
* '''Movies:''' [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Movies/neural.htm#ncrest Neural Movies] | |||
== External Links == | |||
'''Research Labs''' | |||
* University of Michigan [http://www.biology.lsa.umich.edu/research/labs/ktosney/file/Res/ResNc.html Tosney Lab] | |||
* Stowers Institute [http://www.stowers-institute.org/labs/KulesaLab.asp Kulesa Lab] | [http://www.stowers-institute.org/labs/TrainorLab.asp Trainor Lab] | |||
* University College London [http://www.anat.ucl.ac.uk/research/mayor/index.html Mayor Lab] | |||
* University of Iowa [http://www.anatomy.uiowa.edu/pages/directory/faculty/cornell.asp Cornell Lab] | |||
* Washington University in St. Louis, School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics [http://peds.wustl.edu/research/labs/Heuckeroth_Robert_O/ Heuckeroth Lab] | |||
[[Category:Neural Crest]] | |||
==Reference== | |||
<pubmed>10683170</pubmed> | |||
{{Template:2010ANAT2341}} | {{Template:2010ANAT2341}} | ||
[[Category:Neural Crest]] | [[Category:Neural Crest]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:45, 1 September 2010
Neural Crest Development
Introduction
The neural crest are bilaterally paired strips of cells arising in the ectoderm at the margins of the neural tube. These cells migrate to many different locations and differentiate into many cell types within the embryo. This means that many different systems (neural, skin, teeth, head, face, heart, endocrine, gastrointestinal tract) will also have a contribution fron the neural crest cells.
In the body region, neural crest cells also contribute the peripheral nervous system (both neurons and glia) consisting of sensory ganglia (dorsal root ganglia), sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia and neural plexuses within specific tissues/organs.
In the head region, neural crest cells migrate into the pharyngeal arches (as shown in movie below) forming ectomesenchyme contributing tissues which in the body region are typically derived from mesoderm (cartilage, bone, and connective tissue). General neural development is also covered in Neural Notes.
Lecture Objectives
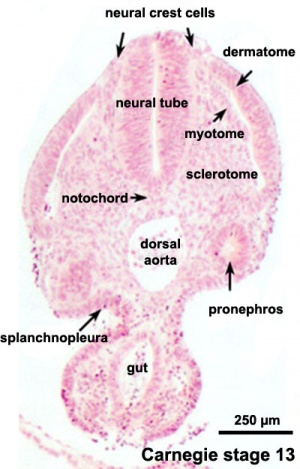
- Understand the structures derived from ectoderm.
- Understand the formation of neural folds.
- Identify the initial location of neural crest cells in the trilaminar embryo.
- Identify pathways of neural crest migration throughout the embryo.
- To know the major tissues to which neural crest cells contribute.
- To know how abnormalities in development that result from abnormal neural crest cell migration.
- Understand how neural crest cells contribute to the pharyngeal arches and the head structures they form.
Textbook References
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 4 p61-63 - p71,75, 385, 392 p393-94 (figure showing cell types); Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240,
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 4 p74-82 - Chapter 5, experimental methods; Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418
- Neural Crest Development
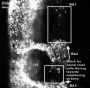
Neural Crest Migration in the Head
Movie Source: Original Neural Crest movies kindly provided by Paul Kulesa.
Related Movies: Migration 01 | Migration 02 | Migration 03 | Migration 04 | Migration 05 | Migration 06 | Migration 07
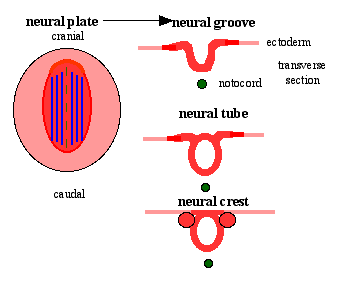
Early Development and Neural Derivatives
- bilaminar embryo- hypoblast
- trilaminar embryo - ectoderm layer
- neural plate - neural groove - neural tube and neural crest
- cranial expansion of neural tube - central nervous system
- caudal remainder of neural tube - spinal cord
Neural Crest - contributes both neural and non-neural cells
- dorsal root ganglia
- parasympathetic / sympathetic ganglia.
Neural Crest Origin
- lateral region of neural plate
- dorsal neural fold->tube
Two main embryo regions
- Head (CNS) - differentiate slightly earlier, mesencephalic region of neural folds
- Body (spinal cord) - lateral edges of fused neural tube
Neural Crest Generation
- cranial region - Begins when still neural fold
- spinal cord - from day 22 until day 26
- after closure of caudal neuropore
- rostro-caudal gradient of differentiation
Studies using the chicken model demonstrated that they are not a segregated population. Interactions between the neural plate and epidermis can generate neural crest cells, since juxtaposition of these tissues at early stages results in the formation of neural crest cells at the interface.
At cranial levels, neuroepithelial cells can regulate to generate neural crest cells when the endogenous neural folds are removed, probably via interaction of the remaining neural tube with the epidermis.
Progenitor cells in the neural folds are multipotent, having the ability to form multiple ectodermal derivatives, including epidermal, neural crest, and neural tube cells the neural crest is an induced population that arises by interactions between the neural plate and the epidermis.
The competence of the neural plate to respond to inductive interactions changes as a function of embryonic age.
(Text from: Bronner-Fraser M PNAS 1996 Sep 3;93(18):9352-7)
Neural Crest Derivatives
Neural crest progenitor cells migrate throughout the embryo and give rise to many different adult cells.
This Includes: ganglia cranial, dorsal root, sympathetic trunk, celiac, renal, plexus in GIT, glia, schwann cells, melanocytes (skin), and adrenal medulla (chromaffin cells).
In the head region neural crest also gives rise to a number of connective tissue structures.
Neural Crest - Head
(see also Head Development Notes)
Mesencephalon and caudal Proencephalon
- parasympathetic ganglia CN III
- connective tissue around eye and nerve
- head mesenchyme
- pia and arachnoid mater
- dura from mesoderm
Mesencephalon and Rhombencephalon
- pharayngeal arches
- look at practical notes on neck and head.
- cartilage rudiments (nose, face, middle ear)
- face
- dermis, smooth muscle and fat
- odontoblasts of developing teeth
Rhombencephalon
- C cells of thyroid
- cranial nerve ganglia
- neurons and glia
- parasympathetic of VII, IX, X
- sensory ganglia of V, VII, VIII, IX, X
Neural Crest- Spinal Cord
- peripheral nervous system
- dorsal root ganglia (sensory N)
- parasympathetic ganglia
- sympathetic ganglia
- motoneurons in both ganglia
- all associated glia
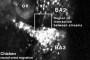
Neural Crest Migration
Head
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Trunk
Cardiac Outflow Tract
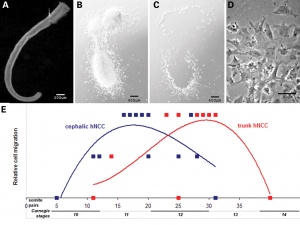
Figure 13.2. Neural crest cell migration in the trunk of the chick embryo
- Neural crest at the level of the body have two general migration pathways, defined by the position of the somite
- medial pathway - between the neural tube and the somite
- lateral pathway - between the somite and the body wall
- A recent study of guidance of neural crest cells (NCC) in mice show migrate 3 specific pathways.
- SEMA3A and its receptor neuropilin 1 (NRP1) - act as repulsive guidance cues
- migration pathway did not affect specification - differs from the concept of migration pathway specifying the neural crest cell differentiation pathway
Neural crest at the level of the head have a different migration pathway. Figure 13.7. Cranial neural crest cell migration in the mammalian head
Sympathetic Ganglia and Adrenal Medulla
Enteric nervous system
Historic Migration Experiments
Key early experiments in understanding the pattern of neural crest migration were carried out by LeDouarin in the 1980's (see Development of the peripheral Nervous system from the neural crest, Ann Rev Cell Biol 4 p375) Quail-Chick Chimeras | Figure 1.11. Neural crest cell migration Chimera experiment
These transplantation studies in chicken/quail chimeras utilised the different nucleoli appearance of cells to differentiate different species. Thus transplanation and subsequent histological processing allowed identification of the migration path and final destination of transplanted neural crest cells.
Similar later experiments have now been carried out using the neural crest cells molecularly tagged with (LacZ).
Abnormalities
Neuroblastoma
Digeorge Syndrome (DGS)
- DiGeorge syndrome is the most frequent microdeletion syndrome in humans caused by a hemizygous deletion (1.5 to 3.0-Mb) of chromosome 22q11.2.
- Velo-cardio-facial syndrome, Hypoplasia of thymus and parathyroids, third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome.
- Abnormalities: cardiovascular, thymic and parathyroid, craniofacial anomalies, renal anomalies, hypocalcemia and immunodeficiency.
Intestinal Aganglionosis
- Intestinal Aganglionosis, Hirschsprung's Disease or Megacolon
- lack of enteric nervous system (neural ganglia) in the intestinal tract responsible for gastric motility (peristalsis).
- severity is dependent upon the amount of the GIT that lacks intrinsic ganglia, due to developmental lack of neural crest migration into those segments.
- first indication in newborns is an absence of the first bowel movement, other symptoms include throwing up and intestinal infections.
- Clinically this is detected by one or more tests (barium enema and x ray, manometry or biopsy) and can currently only be treated by surgery. A temoporary ostomy (Colostomy or Ileostomy) with a stoma is carried out prior to a more permanent pull-through surgery.
Melanoma
- In Australia each year 8,800 people are diagnosed with melanoma, and almost 1000 people die (Data, Cancer Council Australia).
- Two different findings on the reprogramming of melanoma cells, which have a neural crest origin, when transplanted between species into embryos.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (von Recklinghausen) occurs in 1 in 3,000 to 4,000 people with characteristic skin blemishes forming in early childhood.
- Multiple café-au-lait spots (flat skin patches darker than the surrounding area) appear in early childhood which increase in both size and number with age.
- tumors can develop along nerves in the skin, brain, and other parts of the body. In the iris of the eye, Lisch nodules (benign growths) also appear
- (French, café-au-lait = coffee with milk)
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology- Neurofibroma
Tetralogy of Fallot
Cardiac abnormality possibly stemming from abnormal neural crest migration. Named after Etienne-Louis Arthur Fallot (1888) who described it as "la maladie blue". (More? Cardiovascular System Development | Cardiac Tutorial | Lecture - Heart | Heart Abnormalities)
Treacher Collins syndrome
(TCS) A genetic developmental abnormality results from autosomal dominant mutations of the gene TCOF1 encoding the protein Treacle, identified in 2006. The syndrome is characterized by hypoplasia of the facial bones, cleft palate, and middle and external ear defects. These defects may relate to the effects on neural crest migration. (More? Neural Crest Development | OMIM - TCOF1 | PMID: 8563749)
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter Chapter 10 The Pharyngeal Apparatus pp201 - 240.
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 12 Development of the Head, the Neck, the Eyes, and the Ears pp349 - 418.
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 The Cranial Neural Crest | Figure 13.1. Regions of the neural crest | Figure 13.7. Cranial neural crest cell migration in the mammalian head | Figure 13.2. Neural crest cell migration in the trunk of the chick embryo | Figure 13.10. Separation of the truncus arteriosus into the pulmonary artery and aorta | Figure 22.23. Chick embryo rhombomere neural crest cells and their musculoskeletal packets | Figure 13.4. Segmental restriction of neural crest cells and motor neurons by the ephrin proteins of the sclerotome | Figure 1.3. Pharyngeal arches | Table 13.2. Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches
- Neural Crest Experiments: Figure 1.11. Neural crest cell migration Chimera experiment | Figure 13.5. Pluripotency of trunk neural crest cells
- Molecular Biology of the Cell Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter New York and London: Garland Science; c2002 Figure 21-80. The main pathways of neural crest cell migration Figure 21-91. Diagram of a 2-day chick embryo, showing the origins of the nervous system | Figure 19-23. An example of a more complex mechanism by which cells assemble to form a tissue
- Neuroscience Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2001Figure 22.1. Neurulation in the mammalian embryo | Figure 22.12. Cell signaling during the migration of neural crest cells
- Madame Curie Bioscience Database Chapters taken from the Madame Curie Bioscience Database (formerly, Eurekah Bioscience Database) Cranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton | Neural Crest Cells and the Community of Plan for Craniofacial Development: Historical Debates and Current Perspectives | Figure 1. Diagram of an E10 embryo showing the origins of neural crest cells that colonize the developing gastrointestinal tract
- Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects Siegel, George J.; Agranoff, Bernard W.; Albers, R. Wayne; Fisher, Stephen K.; Uhler, Michael D., editors Philadelphia: Lippincott,Williams & Wilkins; c1999Figure 27-10. Neuropoietic model of neural crest cell lineage | Figure 27-11. Growth factor control of neural crest lineage decisions | Figure 27-15. The Schwann cell lineage
Search
- Bookshelf neural crest
- Pubmed neural crest
UNSW Embryology Links
- Notes: Introduction | Abnormalities | Stage 13/14 | Stage 22 | Stage 22 high power | Generation | Migration | Peripheral Ganglia | GIT Enteric | HeartMolecular | Text only | Web Links
- Lectures: ANAT2341 - Embryology 2008 - Lecture 13
- Movies: Neural Movies
External Links
Research Labs
- University of Michigan Tosney Lab
- Stowers Institute Kulesa Lab | Trainor Lab
- University College London Mayor Lab
- University of Iowa Cornell Lab
- Washington University in St. Louis, School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics Heuckeroth Lab
Reference
<pubmed>10683170</pubmed>
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2010
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Lab 1 | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Integumentary | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology 2010 Lecture 12. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_Lecture_12
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ <pubmed>18689800</pubmed>| Hum Mol Genet.
- ↑ <pubmed>18689800</pubmed>| Hum Mol Genet.