2010 BGD Practical 3 - Notochord: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The embryonic structure which establishes body axes and patterns surrounding tissues is called the '''notochord'''. | The embryonic structure which establishes body axes and patterns surrounding tissues is called the '''notochord'''. | ||
The '''notochord''' is a midline column of cells running in a rostrocaudal direction (head-tail) within the mesoderm layer. It exists as a transient developmental patterning structure with a role in molecular signaling (patterning) and controlling the direction of embryonic disc folding (mechanical). | The '''notochord''' is a midline column of cells running in a rostrocaudal direction (head-tail) within the mesoderm layer. It exists as a transient developmental patterning structure with a role in molecular signaling (patterning) and controlling the direction of embryonic disc folding (mechanical). These images are of the embryonic disc in week 3 (stage 7). | ||
[[File:Stage7 axial process.jpg]] | [[File:Stage7 axial process.jpg]] [[File:Mesoderm cartoon1.gif]][[File:Stage11 sem100c.jpg||thumb|stage 11 Embryo]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
# The notochordal canal may appear to break down on the endodermal side forming a notochordal plate continuous with the endodermal layer. | # The notochordal canal may appear to break down on the endodermal side forming a notochordal plate continuous with the endodermal layer. | ||
# Notochordal plate folds to form notochord. The notochord (also called axial mesoderm) is an embryonic structure that regulates differentiation of surrounding structures including the overlying ectoderm (neural plate) and mesoderm (somites). | # Notochordal plate folds to form notochord. The notochord (also called axial mesoderm) is an embryonic structure that regulates differentiation of surrounding structures including the overlying ectoderm (neural plate) and mesoderm (somites). | ||
==Disc Folding== | ==Disc Folding== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:Stage7 folding.jpg|left]] '''Folding:''' all edges of the embryonic disc will fold ventrally, forming a rostro-caudal "C" shaped tube. | [[File:Stage7 folding.jpg|left]] '''Folding:''' all edges of the embryonic disc will fold ventrally, forming a rostro-caudal "C" shaped tube. | ||
{| border='0px' | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Chorion 001 icon.jpg|120px|link=Development Animation - Chorionic Cavity]] | |||
| [[File:Amnion 001 icon.jpg|120px|link=Development Animation - Amniotic Cavity]] | |||
| [[File:Week3_folding icon.jpg|120px|link=Development Animation - Week 3]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Development Animation - Chorionic Cavity|Chorionic Cavity]] | |||
| [[Development Animation - Amniotic Cavity|Amniotic Cavity]] | |||
| [[Development_Animation_-_Week 3|Week 3]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 21:21, 9 May 2010
Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 | Quiz
Introduction
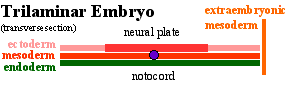
The embryonic structure which establishes body axes and patterns surrounding tissues is called the notochord.
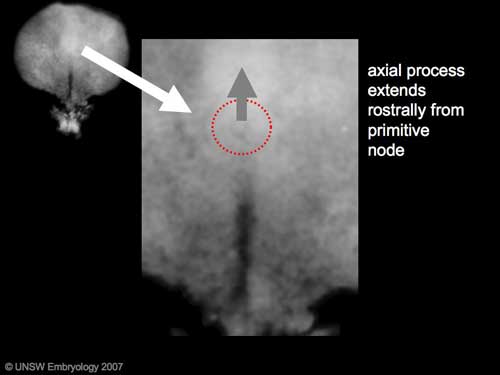
The notochord is a midline column of cells running in a rostrocaudal direction (head-tail) within the mesoderm layer. It exists as a transient developmental patterning structure with a role in molecular signaling (patterning) and controlling the direction of embryonic disc folding (mechanical). These images are of the embryonic disc in week 3 (stage 7).
The notochordal process begins as a fold of ectoderm extending cranially toward the prechordal plate region. The sequence of differentiation: notochordal process -> notochordal plate -> notochord.
- Elongation of the notochordal process cranially from the primitive pit as a hollow tube (notochordal canal) in the midline of the embryonic disc underlying the ectoderm.
- The notochordal canal may appear to break down on the endodermal side forming a notochordal plate continuous with the endodermal layer.
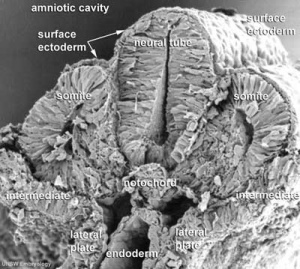
- Notochordal plate folds to form notochord. The notochord (also called axial mesoderm) is an embryonic structure that regulates differentiation of surrounding structures including the overlying ectoderm (neural plate) and mesoderm (somites).
Disc Folding
Folding: all edges of the embryonic disc will fold ventrally, forming a rostro-caudal "C" shaped tube.
| Chorionic Cavity | Amniotic Cavity | Week 3 |
Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 | Quiz
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
- 2010 BGD: Lecture 1 | Lecture 2 | Practical 3 | Practical 6 | Practical 12
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology 2010 BGD Practical 3 - Notochord. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2010_BGD_Practical_3_-_Notochord
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G