2009 Lecture 8
This lecture is an introduction to the development and functions of the placenta.
The placenta (Greek, plakuos = flat cake) named on the basis of this organs appearance. The placenta a mateno-fetal organ which begins developing at implantation of the blastocyst and is delivered with the fetus at birth. Only recently have we begun to understand the many different functions this organ carries out in addition to its role in embryonic nutrition. This lecture follows on the concepts of cardiovascular development covered in the previous lecture.
Lecture Objectives
- Understanding of placental villi development
- Understanding of placental structure
- Understanding of placental functions
- Brief understanding of placental abnormalities
Textbook References
- Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p151-188 Heart, Ch8 p189-228 Vasculature
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch14: p304-349
Other textbooks
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch12; p241-254
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p97-122 Heart, Ch8 p123-146 Vasculature
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Ch13-17: p77-111
UNSW Embryology Links
- Placenta Slides Placenta Lecture 7 2008 | Placenta Lecture 2008 - 1 slide/page | Placenta Lecture 2008 Slides - 4 slides/page | Placenta Lecture 2008 Slides - 6 slides/page
- Placenta Movies Heart Movies | Heart Looping | Atrial Septation | Realignment | Ventricular Septation | Heart Septation Models | Historic Heart Movie |
- Placenta Notes | Postnatal | History - Harvey
- Lecture 8 2008 [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/pdf/ANAT2341L8Placentas1.pdf
- System Notes
- Development Timeline
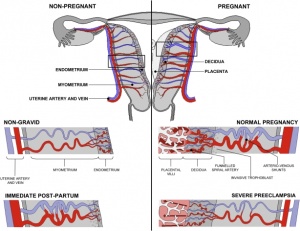
Placental Classification
Classification of placenta is on the basis of histological (microscopic) structural organization and layers between fetal and maternal circulation, giving 3 main groups:
- Haemochorial - placenta where the chorion comes in direct contact with maternal blood (human)
- Endotheliochorial - maternal endometrial blood vessels are bare to their endothelium and these comes in contact with the chorion. (dogs, cats)
- Epitheliochorial - maternal epithelium of the uterus comes in contact with the chorion.considered as primitive (pigs, cows)
The presence of these three differing types of placenta have also been used to describe the pattern mammalian evolution. See also Placental Layers
Placental Types
- Discoid in humans, mice, insectivores, rabbits, rats, and monkeys.
- Zonary in dogs, cats, bears and seals.
- Cotyledenary in cows, deer, goat, and giraffe.
- Diffuse in horses, pigs, camels, lemurs, opossums, kangaroos, and whales
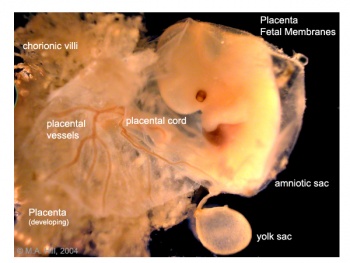
Villi
branched villi - or terminal villi, grow from sides of stem villi, region of main exchange, surrounded by maternal blood in intervillous spaces.
primary villi - week 2, first stage of chorionic villi development, trophoblastic shell cells (syncitiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts) form finger-like extensions into maternal decidua.
secondary villi - week 3, second stage of chorionic villi development, extraembryonic mesoderm grows into villi, covers entire surface of chorionic sac
stem villi - or anchoring villi, cytotrophoblast cells attached to maternal tissue.
tertiary villi third stage of chorionic villi development, mesenchyme differentiates into blood vessels and cells, forms arteriocapillary network, fuse with placental vessels, developing in connecting stalk
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West -
Additional Textbooks
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud
- Essentials of Human Embryology
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald
- Human Embryology and Developmental Biology Carlson
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 - Figure 11.30. Human embryo and placenta after 40 days of gestation | Figure 15.11. Transfer of oxygen from the mother to the fetus in human embryos | Formation of extraembryonic membranes | Figure 15.9. Circulatory system of the early avian embryo
- Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach Nussey, S.S. and Whitehead, S.A. London:Taylor & Francis; c2001
Search
- Bookshelf placenta | placental villi development |
- Pubmed placenta development | placenta | placental villi |
External Links
Placenta Development Terms
- anastomose
- angiogenesis development of new vessels from already existing vessels, this process is secondary to vasculogenesis which is the initial formation of first blood vessels by differentiation of pluripotent mesenchymal cells (extraembryonic mesoderm).
- angioblasts form clusters or blood islands on surface of yolk sac.
- capsularis
- chorionic sac fetal membrane that surrounds the developing embryo.
- cord knotting umbilical cord knotting occurs in 1%, prevents the passage of placental blood. pseudoknots also occur usually with no effect.
- cotyledons maternal side cobblestone appearance, originally placental septa formed grooves is covered with maternal decidua basalis.
- cytotrophoblast extraembryonic cells of trophoblastic shell surrounding embryo, contribute to villi and placental membranes.
- decidua basalis reaction occurs in maternal endometrium at site of, and following, blastocyst implantation. Seen as a deposition of glycogen and proliferation of blood vessels. (see also decidualization)
- decidualization process by which uterine stromal cells differentiate in response to both steroid hormones and embryonic signals into large epitheliod decidual cells. This process is essential for the progress of implantation and establishing fetal-maternal communication.
- endocrine function of placenta:
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum
- Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen, stimulate mammary development
- Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT)
- Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- progesterone and estrogens support maternal endometrium
- relaxin- role in parturition, softens ligaments
- fetal drug addiction occurs when drugs used maternally cross the placental barrier and can establish addiction in the unborn fetus.
- fetal erythroblastosis (Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn), an immune problem from fetus Rh+ /maternal Rh-, leakage from fetus causes anti-Rh antibodies, which is then dangerous for a 2nd child.
- frondosum-
- haemocytoblasts (hemangioblast) stem cells for embryonic blood cell formation, often appearing as a "cluster" or "island".
- Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn - see fetal erythroblastosis.
- hemotrophic nutrition - Term used to describe in late placental development the transfer of blood-borne nutrition from maternal to embryo/fetus compared to early [#histiotrophic_nutrition histiotrophic nutrition]. (More? Uterine glands provide histiotrophic nutrition for the human fetus during the first trimester of pregnancy. Burton GJ, Watson AL, Hempstock J, Skepper JN, Jauniaux E. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jun;87(6):2954-9. PMID: 12050279 | J Clin Endocrinol Metab.)
- histiotrophic nutrition - Term used to describe in early placental development the intital transfer of nutrition from maternal to embryo (histiotrophic nutrition) compared to later blood-borne nutrition ([#hemotrophic_nutrition hemotrophic nutrition]). Histotroph is the nutritional material accumulated in spaces between the maternal and fetal tissues, derived from the maternal endometrium and the uterine glands. This nutritional material is absorbed by phagocytosis initially by blastocyst trophectoderm and then by trophoblast of the placenta. in later placental development nutrition is by the exchange of blood-borne materials between the maternal and fetal circulations, hemotrophic nutrition. (More? Uterine glands provide histiotrophic nutrition for the human fetus during the first trimester of pregnancy. Burton GJ, Watson AL, Hempstock J, Skepper JN, Jauniaux E. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jun;87(6):2954-9. PMID: 12050279 | J Clin Endocrinol Metab.)
- Hofbauer cells - placental villi macrophages of mesenchymal origin with potentially additional functions (vasculogenesis/angiogenesis, villi remodeling, regulation of stromal water content) to their macrophage role.
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin- (hCG) like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum
- Human chorionic somatommotropin - (hCS) or placental lactogen - hormone level increases in maternal blood through pregnancy, decreases maternal insulin sensitivity (raising maternal blood glucose levels and decreasing maternal glucose utilization) aiding fetal nutrition.
- Human chorionic thyrotropin- (hCT) placental derived hormone equivilant to thyroid
- Human chorionic corticotropin- (hCACTH) placental derived hormone equivilant to corticotropin (ACTH) from the pituitary.
- methyldopa - (alpha methyldopa) A central alpha agonist used to lower blood pressure. Used as an antihypertensive drug to lower blood pressure in pre-eclampsia, acting by either a direct or indirect central vasodilatory mechanism. A recent study suggests this drug may have a direct effect on placental and/or endothelial cell function in pre-eclampsia patients, altering angiogenic proteins. Drug commercial brandname (USA) "Aldomet", also available in combination with other drugs: methyldopa and chlorothiazide "Aldochlor", methyldopa and hydrochlorothiazide "Aldoril". (More? [../placenta2.htm#Pre-eclampsia Placenta Abnormalities - Pre-eclampsia] | Medline Plus - Methyldopa | Effect of antihypertensive therapy with alpha methyldopa on levels of angiogenic factors in pregnancies with hypertensive disorders. Khalil A, Muttukrishna S, Harrington K, Jauniaux E. PLoS ONE. 2008 Jul 23;3(7):e2766. PMID: 18648513)
- maternal antibodies- antibodies from the mother's immune system that are capable of crossing placental barrier. They can provide immune protection to the embryo, but may also participate in immune disease (fetal erythroblastosis).
- maternal sinusoids- placental spaces around chorionic villi that are filled with maternal blood. Closest maternal/fetal exchange site.
- Nitabuch's layer (fibrinoid layer) layer formed at maternal/fetal interface during placentation and is thought to act to prevent excessively deep conceptus implantation. Fibrin-type fibrinoid (maternal blood-clot product) and matrix-type fibrinoid (secreted by invasive extravillous trophoblast cells).
- placenta- (Gk. plakuos= flat cake) describes its typical mature discoid shape (20cm diameter and 3 cm thick at term,weighs 500-600 gm).
- placenta accreta- abnormal, adherence with absence of decidua basalis.
- placental arteries- paired, carry deoxygenated blood and waste from the embryo (dorsal aorta->internal iliacs->PA)
- placental blood- blood found within the placental vessels. Obviously part of the fetal blood, but can be collected at birth for theraputic use containing blood stem cells (see cord blood banks).
- placental blood vessels- form initially in the connecting stalk (then umbilical cord), anastomose in chorioni and extend maternally toward chorionic villi, extend embryonically to the sinus venosus and dorsal aorta.
- placental layers- 4 layers separate maternal and fetal blood: syncitiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, villi connective tissue, and fetal capillary endothelium.
- placenta percreta- abnormal, villi penetrate myometrium.
- placenta previa- placenta overlies internal os of uterus, abnormal bleeding, may require cesarian delivery.
- placental veins- paired initially then usually only one left at end of embryonic period, carry oxygenated blood to the embryo (sinus venosus)
- primary villi- develop week 2, consist of trophoblastic shell cells both syncitiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts. Form finger-like extensions into the maternal endometrium.
- protein hormone- usually a protein distributed in the blood that binds to membrane receptors on target cells in different tissues. Do not easliy cross placental barrier.
- relaxin- hormone.
- secondary villi- develop week 3, extraembryonic mesoderm grows into villi, initially covers entire surface of chorionic sac.
- sinus venosus- cavity into which all major embryonic paired veins supply (vitelline, placental, cardinal)
- syncitiotrophoblast- extraembryonic cells of trophoblastic shell surrounding embryo, outside the cytotrophoblast layer, involved with implantation of the blastocyst by eroding extracellular matrix surrounding maternal endometrial cells at site of implantation, also contribute to villi. (dark staining, multinucleated)
- tertiary villi- develop week 4, mesenchyme within secondary villi differentiates into blood vessels and cells, forms arteriocapillary network, fuse with placental vessels developing in connecting stalk.
- trophoblast-
- umbilical cord- fetal attachment cord 1-2 cm diameter, 30-90cm long, covered with amniotic attached to chorionic plate, umbilical vessels (artery, vein) branch into chorionic vessels. Vessels anastomose within the placenta.
- vasculogenesis formation of first blood vessels by differentiation of pluripotent mesenchymal cells (extraembryonic mesoderm) followed by angiogenesis which is the development of new vessels from already existing vessels.
- villi- initially outgrowth of the trophoblastic shell which involve other tissues with development. Develop in sequence (primary, secondary, tertiary) with mature villi being stem por branched type.
- virus- small infectious agent able to cross placental barrier. Can infect embryo and cause developmental abnormalities. (e.g. cytomegalovirus, rubella, measles)
- vitelline- Blood vessels cover entire surface of yolk sac and connect to embryo through yolk stalk
- Arteries- arises from dorsal aorta and contribute to adult GIT arteries.
- Veins- empties into sinus venosus and contribute to the adult portal system.
- waste products- products of cellular metabolism and cellular debris, e.g.- urea, uric acid, bilirubin
- Wharton's jelly placental cord (umbilical cord) gelatinous connective tissue composed of myofibroblast-like stromal cells, collagen fibers, and proteoglycans. Increases in volume (myxomatous, connective tissue embedded in mucus) at parturition to assist closure of placental blood vessels. Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly have recently been identified as a potential source of stem cells. This placental cord substance is named after Thomas Wharton (1614-1673) an English physician and anatomist who first described it.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology 2009 Lecture 8. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_8
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G