2009 Lecture 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
The presence of these three differing types of placenta have also been used to describe the pattern mammalian evolution. See also Placental Layers | The presence of these three differing types of placenta have also been used to describe the pattern mammalian evolution. See also Placental Layers | ||
==Placental Types== | |||
* Discoid in humans, mice, insectivores, rabbits, rats, and monkeys. | * Discoid in humans, mice, insectivores, rabbits, rats, and monkeys. | ||
* Zonary in dogs, cats, bears and seals. | * Zonary in dogs, cats, bears and seals. | ||
* Cotyledenary in cows, deer, goat, and giraffe. | * Cotyledenary in cows, deer, goat, and giraffe. | ||
* Diffuse in horses, pigs, camels, lemurs, opossums, kangaroos, and whales | * Diffuse in horses, pigs, camels, lemurs, opossums, kangaroos, and whales | ||
== Villi == | == Villi == | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 16 August 2009
This lecture is an introduction to the development and functions of the placenta.
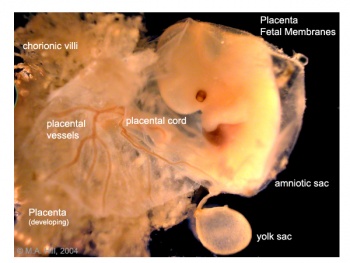
The placenta (Greek, plakuos = flat cake) named on the basis of this organs appearance. The placenta a mateno-fetal organ which begins developing at implantation of the blastocyst and is delivered with the fetus at birth. Only recently have we begun to understand the many different functions this organ carries out in addition to its role in embryonic nutrition. This lecture follows on the concepts of cardiovascular development covered in the previous lecture.
Lecture Objectives
- Understanding of placental villi development
- Understanding of placental structure
- Understanding of placental functions
- Brief understanding of placental abnormalities
Textbook References
- Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p151-188 Heart, Ch8 p189-228 Vasculature
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch14: p304-349
Other textbooks
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch12; p241-254
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p97-122 Heart, Ch8 p123-146 Vasculature
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Ch13-17: p77-111
UNSW Embryology Links
Placental Classification
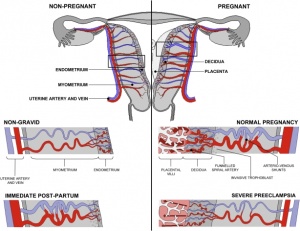
Classification of placenta is on the basis of histological (microscopic) structural organization and layers between fetal and maternal circulation, giving 3 main groups:
- Haemochorial - placenta where the chorion comes in direct contact with maternal blood (human)
- Endotheliochorial - maternal endometrial blood vessels are bare to their endothelium and these comes in contact with the chorion. (dogs, cats)
- Epitheliochorial - maternal epithelium of the uterus comes in contact with the chorion.considered as primitive (pigs, cows)
The presence of these three differing types of placenta have also been used to describe the pattern mammalian evolution. See also Placental Layers
Placental Types
- Discoid in humans, mice, insectivores, rabbits, rats, and monkeys.
- Zonary in dogs, cats, bears and seals.
- Cotyledenary in cows, deer, goat, and giraffe.
- Diffuse in horses, pigs, camels, lemurs, opossums, kangaroos, and whales
Villi
branched villi - or terminal villi, grow from sides of stem villi, region of main exchange, surrounded by maternal blood in intervillous spaces.
primary villi - week 2, first stage of chorionic villi development, trophoblastic shell cells (syncitiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts) form finger-like extensions into maternal decidua.
secondary villi - week 3, second stage of chorionic villi development, extraembryonic mesoderm grows into villi, covers entire surface of chorionic sac
stem villi - or anchoring villi, cytotrophoblast cells attached to maternal tissue.
tertiary villi third stage of chorionic villi development, mesenchyme differentiates into blood vessels and cells, forms arteriocapillary network, fuse with placental vessels, developing in connecting stalk
References
Textbooks
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T.V.N Persaud
- Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West -
Additional Textbooks
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud
- Essentials of Human Embryology
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald
- Human Embryology and Developmental Biology Carlson
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 - Figure 11.30. Human embryo and placenta after 40 days of gestation | Figure 15.11. Transfer of oxygen from the mother to the fetus in human embryos | Formation of extraembryonic membranes | Figure 15.9. Circulatory system of the early avian embryo
- Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach Nussey, S.S. and Whitehead, S.A. London:Taylor & Francis; c2001
Search
- Bookshelf placenta | placental villi development |
- Pubmed placenta development | placenta | placental villi |
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 24) Embryology 2009 Lecture 8. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_8
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G