2009 Lecture 23: Difference between revisions
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
'''Membrane Rupture''' - breaking of the amniotic membrane and release of amniotic fluid (water breaking). | '''Membrane Rupture''' - breaking of the amniotic membrane and release of amniotic fluid (water breaking). | ||
'''Morbidity''' (Latin, ''morbidus'' = "sick" or "unhealthy") refers to a diseased state, disability, or poor health due to any cause. | '''Morbidity''' - (Latin, ''morbidus'' = "sick" or "unhealthy") refers to a diseased state, disability, or poor health due to any cause. | ||
'''Presentation''' - how the fetus is situated in the uterus. | '''Presentation''' - how the fetus is situated in the uterus. | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 13 October 2009
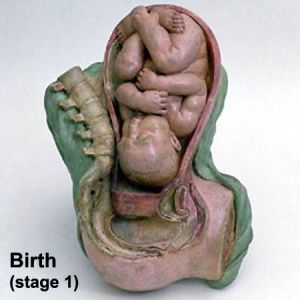
Birth and Postnatal Development
Introduction
There are a great number of comprehensive, scientific and general, books and articles that cover Parturition, Birth or Childbirth.
Birth or parturition is a critical stage in development, representing in mammals a transition from direct maternal support of fetal development, physical expulsion and establishment of the newborns own respiratory, circulatory and digestive systems.
Textbooks
- Human Embryology (2nd ed.) Larson Chapter 15 p471-488
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 7 p129-167
Gestation Period
The median duration of gestation for first births from assumed ovulation to delivery was 274 days (just over 39 weeks). For multiple births, the median duration of pregnancy was 269 days (38.4 weeks).
- "...one should count back 3 months from the first day of the last menses, then add 15 days for primiparas or 10 days for multiparas, instead of using the common algorithm for Naegele's rule." Reference: Mittendorf R, Williams MA, Berkey CS, Cotter PF. The length of uncomplicated human gestation. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jun;75(6):929-32
Historically, Franz Carl Naegele (1777-1851) developed the first scientific rule for estimating length of a pregnany.
Preterm Birth
A study has shown that risks of preterm birth in low abnormal birth weight (intrauterine growth restriction) and high (large for gestational age) categories are 2- to 3-fold greater than the risk among appropriate-for-gestational-age infants.
In another study of placenta previa, low birth weight is due mainly to preterm delivery and to a lesser extent with fetal growth restriction.
Reference: Lackman F, Capewell V, Richardson B, daSilva O, Gagnon R. The risks of spontaneous preterm delivery and perinatal mortality in relation to size at birth according to fetal versus neonatal growth standards. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Apr;184(5):946-53.
Ananth CV, Demissie K, Smulian JC, Vintzileos AM. Relationship among placenta previa, fetal growth restriction, and preterm delivery: a population-based study. Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Aug;98(2):299-306.
Abnormalities
Labor Abnormalities
- Premature Labor - occurs 7 -10% in humans, contributes 75% perinatal mortalities
- Underdeveloped Systems - particularly respiratory, surfactant, hyaline membrane disease (see respiratory development lecture)
Placental Abnormalities
- placenta accreta - abnormal adherence, with absence of decidua basalis
- placenta percreta - villi penetrate myometrium
- placenta previa - placenta overlies internal os of uterus, abnormal bleeding, cesarian delivery
Breech Delivery
- Historically, breech-born children were called agrippi, meaning "delivered with difficulty" (aegre parti).
- Breech position - occurs in about 3% of fetuses when buttocks or lower limb are presented to the birth canal rather than normal cephalic (head-first) position (presentation).
- Associated increased - perinatal mortality, perinatal morbidity, recurrence in successive siblings
Current research suggests that genetically that both men and women delivered in breech presentation at term could also contribute to an increased risk of breech delivery in their offspring. ([#18369204 Nordtveit TI, etal., 2008])
Links
- UNSW Embryology Introduction | Birth Overview | Abnormalities | Caesarean | Apgar | Premature | Low Birth Weight | Placental Cord Clamping | Cardiovascular | Stillbirth and Perinatal Death | Molecular Web Links
Birth Terms
Amniotomy - birth medical procedure thought to speed labor, where the amniotic sac is artificially ruptured using a tool (amniohook).
Breech - fetal buttocks presented first and can also occur in different forms depending on presentation (complete breech, frank breech, footing breech, knee breech).
Decidual Activation - increased uterine proteolysis and extracellular matrix degradation.
Dilatation - opening of the cervix in preparation for birth (expressed in centimetres).
Effacement - shortening or thinning of the cervix, in preparation for birth.
Forceps - mechanical "plier-like" tool used on fetal head to aid birth.
Fetal Macrosomia - clinical description for a fetus that is too large, condition increases steadily with advancing gestational age and defined by a variety of birthweights. In pregnant women anywhere between 2 - 15% have birth weights of greater than 4000 grams (4 Kg, 8 lb 13 oz).
Membrane Rupture - breaking of the amniotic membrane and release of amniotic fluid (water breaking).
Morbidity - (Latin, morbidus = "sick" or "unhealthy") refers to a diseased state, disability, or poor health due to any cause.
Presentation - how the fetus is situated in the uterus.
Presenting part - part of fetus body that is closest to the cervix.
Second stage of labour - passage of the baby through the birth canal into the outside world.
Vacuum Extractor - suction cap device used on fetal head to aid birth.
Vertex Presentation (cephalic presentation) where the fetus head is the presenting part, most common and safest birth position.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Course Content 2009
Embryology Introduction | Cell Division/Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1&2 Development | Week 3 Development | Lab 2 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Lab 3 | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Lab 4 | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Lab 5 | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Lab 6 | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Lab 7 | Kidney | Genital | Lab 8 | Sensory - Ear | Integumentary | Lab 9 | Sensory - Eye | Endocrine | Lab 10 | Late Vascular Development | Fetal | Lab 11 | Birth, Postnatal | Revision | Lab 12 | Lecture Audio | Course Timetable
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology 2009 Lecture 23. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2009_Lecture_23
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G