2009 Lecture 2: Difference between revisions
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Cell Division== | ==Cell Division== | ||
===Mitosis=== | ===Mitosis=== | ||
== '''Cell Division''' == | |||
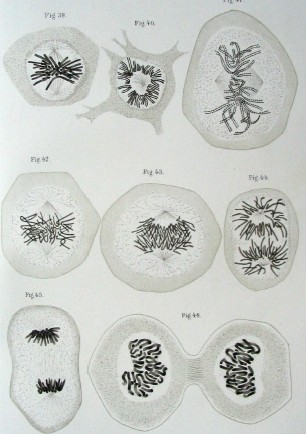
[[Image:Historic 1882 mitosis drawing.jpg]] | |||
Historic Historic 1882 mitosis drawings | |||
==Introduction== | |||
How does one cell become two? | |||
'''Movies''' | |||
* JCB - Movie Collection [http://jcb.rupress.org/misc/annotatedvideo.shtml#Mitosis Mitosis] | [http://jcb.rupress.org/misc/annotatedvideo.shtml#Cytokinesis Cytokinesis] | |||
* '''2008''' ANAT3231 Lecture PDF lecture14-15 [http://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/units/pdf/08L14-15s1.pdf 1 slide/page (view)] | [http://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/units/pdf/08L14-15s4.pdf 4 slides/page (print)] | [http://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/units/pdf/08L14-15s6.pdf 6 slides/page (print)] | [http://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/units/pdf/08L14-15txt.pdf text (print)] | |||
==Cell Division== | |||
* [http://www.nature.com/celldivision/milestones/index.html Cell Division Milestones] | |||
* Recent Nobel Prizes | |||
Features 2 mechanical processes | |||
* Mitosis segregation of chromosomes and formation of 2 nuclei | |||
* Cytokinesis splitting of the cell as a whole into 2 daughter cells | |||
==Cell Changes== | |||
* Nucleus | |||
** Chromosome condensation | |||
** Nuclear envelope breakdown | |||
* Cytoplasm | |||
** Cytoskeleton reorganization | |||
** Spindle formation (MT) Contractile ring (MF) | |||
** Organelle redistribution | |||
==Mitosis Phases== | |||
* Based on light microscopy of living cells light and electron microscopy of fixed and stained cells | |||
* 5 Phases - prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase | |||
** Cytokinesis 6th stage overlaps the end of mitosis | |||
Movie: Cell Division Animation | |||
Cell Cycle | |||
Overview | |||
Mitosis- Interphase Not a mitotic phase (discussed in cell cycle) | |||
Chromosomes dispersed in nucleus | |||
Gene expression | |||
Cytoskeleton and cell organelles | |||
Distributed and functioning | |||
Mitochondria undergo independent proliferation/division | |||
==Chromosome Changes== | |||
[[Image:Mitosis fl.jpg]] | |||
===Prophase === | |||
* Chromosome DNA has been earlier duplicated (S Phase) | |||
* Chromosomes begin condensing | |||
* Chromosome pairs (chromatids) held together at centromere | |||
* Microtubules disassemble | |||
* Mitotic spindle begins to form | |||
At end of prophase nuclear envelope breaks down | |||
===Prometaphase=== | |||
* Microtubules now enter nuclear region | |||
* Nuclear envelope forms vesicles around mitotic spindle | |||
* Kinetochores form on centromere attach to some MTs of spindle | |||
At end of prometaphase chromosomes move to metaphase plate | |||
Movie: Embryo Mitosis | |||
Movie: Astral Microtubules Microtubule Organisation | |||
Movie: Microtubules Mitotic Spindle | |||
Kinetochore | |||
Kinetochore Movement Movie: Mitotic Spindle- Kinetochore | |||
===Metaphase=== | |||
* Kinetochore MTs align chromosomes in one midpoint plane | |||
Metaphase ends when sister kinetochores separate | |||
===Anaphase=== | |||
[[Image:Chromosome_motility_anaphase.jpg|thumb|Chromosome motility anaphase]] | |||
* Separation of sister Kinetochores | |||
* shortening of Kinetochore microtubules pulls chromosome to spindle pole | |||
Anaphase ends as nuclear envelope (membrane) begins to reform | |||
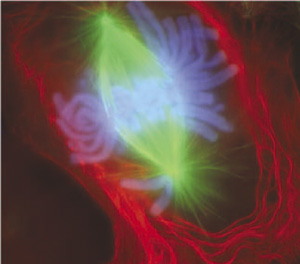
Two telophase HeLa cells expressing GFP–tagged human Aurora B Microtubules - red inner-centromere protein - blue Aurora B–GFP - green DNA - white | |||
===Telophase=== | |||
* Chromosomes arrive at spindle poles | |||
* Kinetochore MTs lost | |||
* Condensed chromosomes begin expanding | |||
** Continues through cytokinesis | |||
===Cytokinesis=== | |||
* Division of cytoplasmic contents | |||
* Contractile ring forms at midpoint under membrane | |||
* Microfilament ring Contracts forming cleavage furrow | |||
* Eventually fully divides cytoplasm | |||
== Cell Organelles == | |||
===Mitochondria=== | |||
* Divide independently of cell mitosis | |||
* distributed into daughter cells | |||
===Peroxisomes=== | |||
* localise at spindle poles | |||
===Endoplasmic Reticulum=== | |||
===Golgi=== | |||
[[Image:Post-mitotic Golgi stack formation.png|thumb|Post-mitotic Golgi stack formation]] | |||
* 2 processes - disassembly and reassembly | |||
* Golgi stack undergoes a continuous fragmentation process | |||
* fragments are distributed into daughter cells | |||
* are reassembled into new Golgi stacks | |||
'''Disassembly''' | |||
* Unstacking - mediated by two mitotic kinases (cdc2 and plk) | |||
* Vesiculation - mediated by COPI budding machinery ARF1 and the coatomer complex | |||
'''Reassembly''' | |||
* Fusion - formation of single cisternae by membrane fusion | |||
* Restacking - requires dephosphorylation of Golgi stacking proteins by protein phosphatase PP2A | |||
Links: Tang D, Mar K, Warren G, Wang Y. Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined reconstitution assay. J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6085-94. Epub 2007 Dec 21. PMID: 18156178 | |||
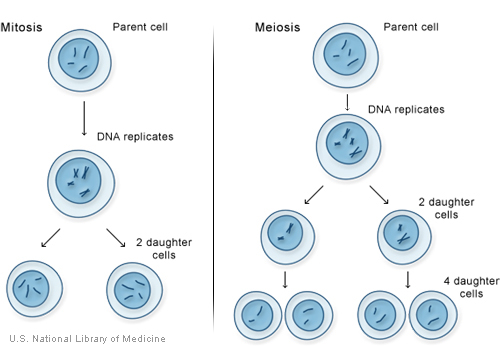
==Mitosis and Meiosis== | |||
[[Image:Mitosis meiosis1.jpg]] | |||
Progeny | |||
Mitosis 2 Daughter cells identical to parent (diploid) | |||
Meiosis Germ cell division (haploid) | |||
* Reductive division | |||
* Generates haploid gametes (egg, sperm) | |||
* Each genetically distinct from parent | |||
* Genetic recombination (prophase 1) | |||
** Exchanges portions of chromosomes maternal/paternal homologous pairs | |||
* Independent assortment of paternal chromosomes (meiosis 1) | |||
Cell Birth - Mitosis and Meiosis 1st cell division- Meiosis | |||
Homologous chromosomes pairing unique to meiosis | |||
* Each chromosome duplicated and exists as attached sister chromatids before pairing occurs | |||
* Genetic Recombination shown by chromosomes part red and part black | |||
** chromosome pairing in meiosis involves crossing-over between homologous chromosomes | |||
(For clarity only 1 pair of homologous chromosomes shown) | |||
===Comparison of Meiosis/Mitosis=== | |||
* After DNA replication 2 nuclear (and cell) divisions required to produce haploid gametes | |||
* Each diploid cell in meiosis produces 4 haploid cells (sperm) 1 haploid cell (egg) | |||
* Each diploid cell mitosis produces 2 diploid cells | |||
===Abnormalities=== | |||
'''Meiotic Nondisjunction''' | |||
* Occurs when homologues fail to separate during meiotic division I or II | |||
* Down Syndrome | |||
* Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 | |||
'''Chromosomal Translocations''' | |||
* Philadelphia chromosome | |||
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia | |||
** Piece of Chr9 exchanged with Chr22 Generates truncated abl | |||
Overstimulates cell production | |||
===Meiosis Sex Differences=== | |||
'''Female''' (oogenesis) | |||
* Meiosis initiated once in a finite population of cells | |||
* 1 gamete produced / meiosis | |||
* Completion of meiosis delayed for months or years | |||
* Meiosis arrested at 1st meiotic prophase and reinitiated in a smaller population of cells | |||
* Differentiation of gamete occurs while diploid in first meiotic prophase | |||
* All chromosomes exhibit equivalent transcription and recombination during meiotic prophase | |||
'''Male''' (spermatogenesis) | |||
* Meiosis initiated continuously in a mitotically dividing stem cell population | |||
* 4 gametes produced / meiosis | |||
* Meiosis completed in days or weeks | |||
* Meiosis and differentiation proceed continuously without cell cycle arrest | |||
* Differentiation of gamete occurs while haploid after meiosis ends | |||
Sex chromosomes excluded from recombination and transcription during first meiotic prophase | |||
===Meiosis=== | ===Meiosis=== | ||
== Fertilization == | == Fertilization == | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 27 July 2009
Cell Division and Fertilization
This lecture will introduce two key concepts of biology, cell division and cellular sexual development.
Cell Division
Mitosis
Cell Division
Historic Historic 1882 mitosis drawings
Introduction
How does one cell become two?
Movies
- JCB - Movie Collection Mitosis | Cytokinesis
- 2008 ANAT3231 Lecture PDF lecture14-15 1 slide/page (view) | 4 slides/page (print) | 6 slides/page (print) | text (print)
Cell Division
- Cell Division Milestones
- Recent Nobel Prizes
Features 2 mechanical processes
- Mitosis segregation of chromosomes and formation of 2 nuclei
- Cytokinesis splitting of the cell as a whole into 2 daughter cells
Cell Changes
- Nucleus
- Chromosome condensation
- Nuclear envelope breakdown
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoskeleton reorganization
- Spindle formation (MT) Contractile ring (MF)
- Organelle redistribution
Mitosis Phases
- Based on light microscopy of living cells light and electron microscopy of fixed and stained cells
- 5 Phases - prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
- Cytokinesis 6th stage overlaps the end of mitosis
Movie: Cell Division Animation
Cell Cycle
Overview
Mitosis- Interphase Not a mitotic phase (discussed in cell cycle) Chromosomes dispersed in nucleus Gene expression Cytoskeleton and cell organelles Distributed and functioning Mitochondria undergo independent proliferation/division
Chromosome Changes
Prophase
- Chromosome DNA has been earlier duplicated (S Phase)
- Chromosomes begin condensing
- Chromosome pairs (chromatids) held together at centromere
- Microtubules disassemble
- Mitotic spindle begins to form
At end of prophase nuclear envelope breaks down
Prometaphase
- Microtubules now enter nuclear region
- Nuclear envelope forms vesicles around mitotic spindle
- Kinetochores form on centromere attach to some MTs of spindle
At end of prometaphase chromosomes move to metaphase plate
Movie: Embryo Mitosis
Movie: Astral Microtubules Microtubule Organisation
Movie: Microtubules Mitotic Spindle
Kinetochore
Kinetochore Movement Movie: Mitotic Spindle- Kinetochore
Metaphase
- Kinetochore MTs align chromosomes in one midpoint plane
Metaphase ends when sister kinetochores separate
Anaphase
- Separation of sister Kinetochores
- shortening of Kinetochore microtubules pulls chromosome to spindle pole
Anaphase ends as nuclear envelope (membrane) begins to reform
Two telophase HeLa cells expressing GFP–tagged human Aurora B Microtubules - red inner-centromere protein - blue Aurora B–GFP - green DNA - white
Telophase
- Chromosomes arrive at spindle poles
- Kinetochore MTs lost
- Condensed chromosomes begin expanding
- Continues through cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
- Division of cytoplasmic contents
- Contractile ring forms at midpoint under membrane
- Microfilament ring Contracts forming cleavage furrow
- Eventually fully divides cytoplasm
Cell Organelles
Mitochondria
- Divide independently of cell mitosis
- distributed into daughter cells
Peroxisomes
- localise at spindle poles
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi
- 2 processes - disassembly and reassembly
- Golgi stack undergoes a continuous fragmentation process
- fragments are distributed into daughter cells
- are reassembled into new Golgi stacks
Disassembly
- Unstacking - mediated by two mitotic kinases (cdc2 and plk)
- Vesiculation - mediated by COPI budding machinery ARF1 and the coatomer complex
Reassembly
- Fusion - formation of single cisternae by membrane fusion
- Restacking - requires dephosphorylation of Golgi stacking proteins by protein phosphatase PP2A
Links: Tang D, Mar K, Warren G, Wang Y. Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined reconstitution assay. J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6085-94. Epub 2007 Dec 21. PMID: 18156178
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis 2 Daughter cells identical to parent (diploid)
Meiosis Germ cell division (haploid)
- Reductive division
- Generates haploid gametes (egg, sperm)
- Each genetically distinct from parent
- Genetic recombination (prophase 1)
- Exchanges portions of chromosomes maternal/paternal homologous pairs
- Independent assortment of paternal chromosomes (meiosis 1)
Cell Birth - Mitosis and Meiosis 1st cell division- Meiosis
Homologous chromosomes pairing unique to meiosis
- Each chromosome duplicated and exists as attached sister chromatids before pairing occurs
- Genetic Recombination shown by chromosomes part red and part black
- chromosome pairing in meiosis involves crossing-over between homologous chromosomes
(For clarity only 1 pair of homologous chromosomes shown)
Comparison of Meiosis/Mitosis
- After DNA replication 2 nuclear (and cell) divisions required to produce haploid gametes
- Each diploid cell in meiosis produces 4 haploid cells (sperm) 1 haploid cell (egg)
- Each diploid cell mitosis produces 2 diploid cells
Abnormalities
Meiotic Nondisjunction
- Occurs when homologues fail to separate during meiotic division I or II
- Down Syndrome
- Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
Chromosomal Translocations
- Philadelphia chromosome
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Piece of Chr9 exchanged with Chr22 Generates truncated abl
Overstimulates cell production
Meiosis Sex Differences
Female (oogenesis)
- Meiosis initiated once in a finite population of cells
- 1 gamete produced / meiosis
- Completion of meiosis delayed for months or years
- Meiosis arrested at 1st meiotic prophase and reinitiated in a smaller population of cells
- Differentiation of gamete occurs while diploid in first meiotic prophase
- All chromosomes exhibit equivalent transcription and recombination during meiotic prophase
Male (spermatogenesis)
- Meiosis initiated continuously in a mitotically dividing stem cell population
- 4 gametes produced / meiosis
- Meiosis completed in days or weeks
- Meiosis and differentiation proceed continuously without cell cycle arrest
- Differentiation of gamete occurs while haploid after meiosis ends
Sex chromosomes excluded from recombination and transcription during first meiotic prophase
Meiosis
Fertilization
UNSW Embryology Links
Next Lecture
- Dr Mark Hill 2009 UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G