File:Unilateral microphthalmia patient with delection of SOX2 gene.png
Unilateral_microphthalmia_patient_with_delection_of_SOX2_gene.png (439 × 205 pixels, file size: 126 KB, MIME type: image/png)
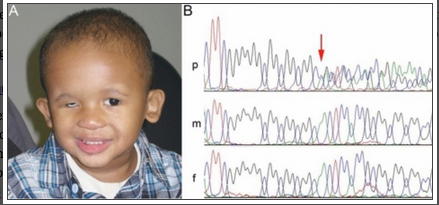
This is a patient with micophthalmia and was caused by the deletion of the SOX2 gene sequence. When compared to his parents, the absence of the gene sequence is more obvious (red arrow), whereas in his parent's genome, the SOX2 gene is normal and present. [1]
Identification of a c.70del20 mutation in a patient with unilateral microphthalmia. A: Photograph of Patient 1 with SOX2 anophthalmia syndrome. Note right microphthalmia (prosthesis in place) and prominent ears. B: Sequence fragments showing the c.70del20 region in the patient (p), his mother (m) and his father (f). The position of the deletion is indicated with a red arrow. Note normal SOX2 sequence in the patient’s parents consistent with their unaffected status.
Copyright © 2010 Molecular Vision. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
reference
- ↑ <pubmed>20454695</pubmed>
- Note - This image was originally uploaded as part of an undergraduate science student project and may contain inaccuracies in either description or acknowledgements. Students have been advised in writing concerning the reuse of content and may accidentally have misunderstood the original terms of use. If image reuse on this non-commercial educational site infringes your existing copyright, please contact the site editor for immediate removal.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:47, 23 September 2012 |  | 439 × 205 (126 KB) | Z3331330 (talk | contribs) | This is a patient with micophthalmia and was caused by the deletion of the SOX2 gene sequence. When compared to his parents, the absence of the gene sequence is more obvious (red arrow), whereas in his parent's genome, the SOX2 gene is normal and present. |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: