File:Gray1029.jpg
Gray1029.jpg (700 × 435 pixels, file size: 75 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
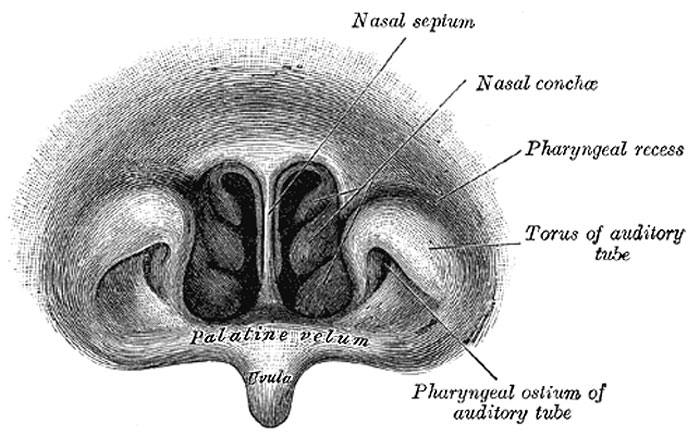
Front of nasa part of Pharynx
As seen with the laryngoscope.
Nasal Part of the Pharynx (pars nasalis pharyngis; nasopharynx) lies behind the nose and above the level of the soft palate: it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx in that its cavity always remains patent. In front (Fig. 1029) it communicates through the choanæ with the nasal cavities. On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal ostium of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape, and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the torus or cushion, caused by the medial end of the cartilage of the tube which elevates the mucous membrane. A vertical fold of mucous membrane, the salpingopharyngeal fold, stretches from the lower part of the torus; it contains the Salpingopharyngeus muscle. A second and smaller fold, the salpingopalatine fold, stretches from the upper part of the torus to the palate. Behind the ostium of the auditory tube is a deep recess, the pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosenmüller). On the posterior wall is a prominence, best marked in childhood, produced by a mass of lymphoid tissue, which is known as the pharyngeal tonsil. Above the pharyngeal tonsil, in the middle line, an irregular flask-shaped depression of the mucous membrane sometimes extends up as far as the basilar process of the occipital bone; it is known as the pharyngeal bursa.
Oral Part of the Pharynx (pars oralis pharyngis) reaches from the soft palate to the level of the hyoid bone. It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the two palatine arches, is the palatine tonsil.
Laryngeal Part of the Pharynx (pars laryngea pharyngis) reaches from the hyoid bone to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, where it is continuous with the esophagus. In front it presents the triangular entrance of the larynx, the base of which is directed forward and is formed by the epiglottis, while its lateral boundaries are constituted by the aryepiglottic folds. On either side of the laryngeal orifice is a recess, termed the sinus piriformis, which is bounded medially by the aryepiglottic fold, laterally by the thyroid cartilage and hyothyroid membrane.
- Gray's Images: Development | Lymphatic | Neural | Vision | Hearing | Somatosensory | Integumentary | Respiratory | Gastrointestinal | Urogenital | Endocrine | Surface Anatomy | iBook | Historic Disclaimer
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
| iBook - Gray's Embryology | |
|---|---|
|
|
Reference
Gray H. Anatomy of the human body. (1918) Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology Gray1029.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Gray1029.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:52, 25 February 2013 |  | 700 × 435 (75 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Front of nasa part of Pharynx== As seen with the laryngoscope. The Nasal Part of the Pharynx (pars nasalis pharyngis; nasopharynx) lies behind the nose and above the level of the soft palate: it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: