File:Female reproductive tract Wnt4.jpg
Original file (1,000 × 563 pixels, file size: 79 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
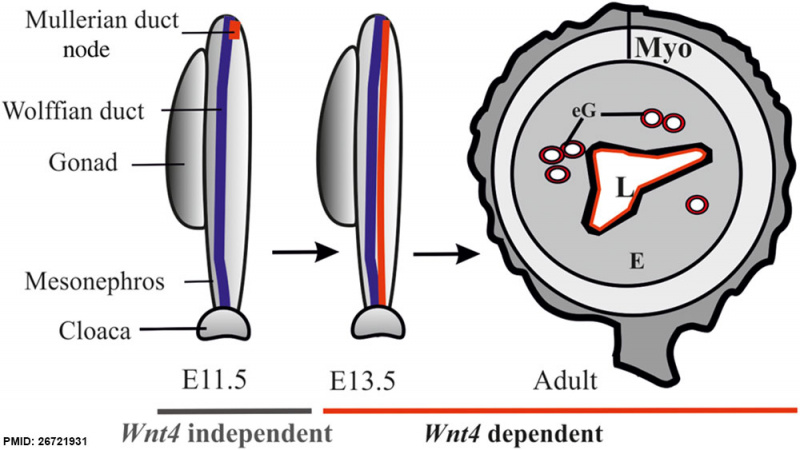
Processes regulated by Wnt4 during female reproductive tract development
Wnt4 is required during prenatal and postnatal development of female reproductive tract. The initial MD primordium occurs independently of Wnt4 function (E11.5, the MD primordium in red). After initiation of the process, differentiation of the MD tip cells, prenatal elongation of the MD and postnatal formation of the endometrial gland (eG) all depend on Wnt4 signalling.
The daughter cells that are initially Wnt4+ contribute to MD and eG formation.
Myo, myometrium; E, endometrium; eG, endometrial glands; L, lumen.
- Links: Vagina Development | Uterus Development
Reference
Prunskaite-Hyyryläinen R, Skovorodkin I, Xu Q, Miinalainen I, Shan J & Vainio SJ. (2016). Wnt4 coordinates directional cell migration and extension of the Müllerian duct essential for ontogenesis of the female reproductive tract. Hum. Mol. Genet. , 25, 1059-73. PMID: 26721931 DOI.
Copyright
Prunskaite-Hyyryläinen, Renata; Skovorodkin, Ilya
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. You are not required to obtain permission to reuse this article.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology Female reproductive tract Wnt4.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Female_reproductive_tract_Wnt4.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:39, 20 March 2017 |  | 1,000 × 563 (79 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: