Talk:BGD Lecture - Face and Ear Development: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " == Introduction == thumb The face is the anatomical feature which is truly unique to each human, though the basis of its general development is ide...") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==2019== | |||
ILI redevelopment. | |||
== | ==2016== | ||
Removed these images | |||
<gallery> | |||
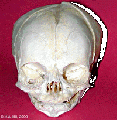
File:Skull anterior.gif|Anterior (anterior fontenelle, sutures, mandible) | |||
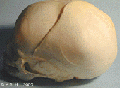
File:Skull_superior.gif|Superior (anterior fontenelle, sutures) | |||
File:Skull lateral view.gif|Lateral view ( suture, mandible) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Original movie media player format | |||
<mediaplayer width='410' height='340' image="http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/images/7/7d/Chicken-neural-crest-migration-01.jpg">File:Chicken-neural crest migration 01.mp4</mediaplayer> | |||
== | ==2013== | ||
* [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php?title=BGD_Lecture_-_Face_and_Ear_Development&oldid=122946 2013] | |||
==2012 == | |||
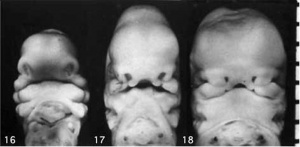
[[File:Stage16-18 face.jpg|thumb]] | |||
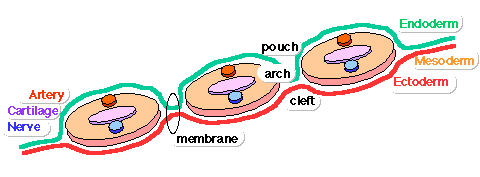
[[ | [[File:Pharyngeal arch structure cartoon.gif]][[File:Stage13 pharyngeal arch excerpts.gif|300px]] | ||
===Textbooks=== | |||
* '''Before We Are Born''' (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 20: p460-479 | |||
* '''Essentials of Human Embryology''', Larson Chapter 12: p252-272 | |||
===Online Textbooks=== | |||
* '''Developmental Biology''' (6th ed.) Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=dbio.figgrp.5455%20 Evolution of the mammalian middle ear bones from the reptilian jaw] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=dbio.figgrp.5460 Chick embryo rhombomere neural crest cells] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=dbio.table.3135 Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowSection&rid=dbio.section.2871 Formation of the Neural Tube] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowSection&rid=dbio.section.2884 Differentiation of the Neural Tube] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowSection&rid=dbio.section.2894 Tissue Architecture of the Central Nervous System] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowSection&rid=dbio.section.2908 Neuronal Types] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowSection&rid=dbio.section.2937 Snapshot Summary: Central Nervous System and Epidermis] | |||
The | * '''Neuroscience''' Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc. ; c2001 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.chapter.879 The Auditory System] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.section.894 The Inner Ear] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.section.893 The Middle Ear] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.section.891 The External Ear] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.chapter.1447 Early Brain Development] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.chapter.1546 Construction of Neural Circuits] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=neurosci.chapter.1640 Modification of Brain Circuits as a Result of Experience] | ||
* ''' | * '''Molecular Biology of the Cell''' (4th Edn) Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter. New York: Garland Publishing; 2002. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.section.3963 Neural Development] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.figgrp.3966 The three phases of neural development] | ||
The [[ | * '''Clinical Methods''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=cm.chapter.1949 63. Cranial Nerves IX and X: The Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=cm.chapter.3847 The Tongue] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=cm.chapter.3777 126. The Ear and Auditory System] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=cm.chapter.3627#3654 An Overview of the Head and Neck - Ears and Hearing] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=cm.chapter.3897 Audiometry] | ||
* '''Health Services/Technology Assessment Text (HSTAT)''' Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), 2003 Oct. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=hstat1a.section.25014#25029 Developmental Disorders Associated with Failure to Thrive] | |||
* '''Eurekah Bioscience Collection'''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=eurekah.chapter.53006 Cranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton] | |||
===Search === | |||
* '''Bookshelf''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books&cmd=search&term=hearing+development hearing development] | |||
* '''Pubmed''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/gquery?itool=toolbar&cmd=search&term=hearing+development hearing development] | |||
==Links== | |||
* NIDCD - [http://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/balance/balance_disorders.asp Balance Disorders] | |||
== | == Terms == | ||
'''altricial animal''' - Term used to describe an animal born in a helpless state, with incomplete development of sensory systems at birth. For example rats and mice are born with incomplete development of visual and auditory systems. | |||
'''ampulla''' - Term used to describe an anatomical dilation of a tube or canal lumen. Anatomical description of the opening end of the uterine tube lying above the ovary and the enlarged initial segmeny of the semicircular canals of the inner ear vestibular system. (More? [ear6.htm Inner Ear] | [genitalXXuterus.htm Genital System - Female Uterus]) | |||
'''aneurism''' - (Greek, ''aneurysma'' = a widening, aneurysm) A term used to describe an abnormal widening of a vessel or anatomical tubal structure. | |||
'''aquaeductus vestibuli '''- see vestibular aqueduct | |||
'''auditory neuropathy''' - (AN) abnormality of transmission of sound information to the brain. | |||
'''auditory tube '''- (eustachian tube) between the middle ear and oral cavity, has a bony (tympanic 1/3) and cartilaginous (pharyngeal 2/3) portion. The main role is equalization of pressure and fluid drainage in the middle ear. | |||
'''auricular hillock '''- see hillock | |||
'''atresia''' - narrowing, usually of an anatomical tube or cavity. | |||
== | '''autophagocytosis''' - (Greek, auto = self, phagy = eating, also called autophagy) a cell death mechanism that uses the cell's own lysosomes to self digest. | ||
'''border cells''' - columnar cells within the organ of Corti on the medial portion of the basilar membrane. | |||
'''canalis reuniens''' - (ductus reuniens, canaliculus reuniens, canalis reuniens, Hensen's canal, Hensen's duct, uniting canal, canalis reuniens of Hensen) short narrow canal connecting the cochlea duct to the saccule. (Victor Hensen, 1835-1924) | |||
'''cerumen''' - (ear wax) produced by glands in the skin of the outer portion of the ear canal. | |||
'''chondrified''' - the developmental differentiation of cartilage from mesenchye, an embryonic connective tissue. | |||
'''cristae ampullaris''' - located in the ampulla of the membranous semicircular canals a region with both supporting and hair cells. The hair cell cilia are embedded in the gelatinous cupula. | |||
'''claudius cells '''- (cells of Claudius) columnar cells with microvilli overlying the basilar membrane and extend from Hensen's cells to the spiral prominence. Barrier cells that lie external to the organ of corti in endolymph. | |||
'''cochlear sac '''- embryonic structure, which will form the coiled cochlear duct and contribute to the saccule. | |||
'''cochlear aqueduct''' - a bony channel containing the fibrous periotic duct. It connects the basal turn of the cochlea perilymphatic space with the subarachnoid space of the posterior cranial cavity. | |||
'''cochlin''' - major constituent of the inner ear extracellular matrix. | |||
'''collagen type II''' - major constituent of the inner ear extracellular matrix. | |||
'''conductive loss''' - term used to describe one of the two major classes of hearing loss involving external and middle ear abnormalities (other form is Sensorineural loss). | |||
'''connexins '''- channel proteins of the gap junctions that allow rapid communication between adjacent cells. The two connexins Cx26 and Cx30 are the major proteins of cochlear gap junctions. | |||
'''connexin 26''' - A strikingly high proportion (50%) of congenital bilateral nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness cases have been linked to mutations in the GJB2 coding for the connexin26 | |||
'''cupular deposits''' - basophilic material on the cupulae of the semicircular ducts, an postnatal ageing phenomenon seen in some vestibular labyrinth. | |||
'''clinical weeks''' - taken from last menstrual period (LMP) and therefore approximately two weeks before fertilization occurs. | |||
Deiters' cells | |||
'''discoidin domain receptor 1''' - (DDR1) a tyrosine kinase receptor activated by native collagen, expressed in the basement membrane and with fibrillar collagens. Found in basal cells of the stria vascularis, type III fibrocytes, and cells lining the basilar membrane of the organ of Corti. {Meyer zum Gottesberge, 2008 #1877} | |||
ductus utriculosaccularis - | |||
'''endochondral ossification''' - the process of bone formation from a pre-existing cartilage template. | |||
endoderm - | |||
endolymphatic fluid - | |||
'''endolymphatic sac''' - inner ear structure that has anatomically both an intraosseous and extraosseous component. Th e sac has functions regulating endolymph that are both secretory and absorptive. Also the site of endolymphatic sac tumors either sporadical occurring or associated with the autosomal-dominant von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease, due to a germ line mutation. | |||
'''embryological weeks''' - taken from the time of fertilization which typically occurs around the middle (day 14), or just after, of the typical 28 day menstrual cycle. | |||
'''Emx2''' - homeobox gene affecting middle ear and inner ear development. | |||
'''eustachian tube''' - (auditory tube) A cavity linking the pharynx to the middle ear, which develops from the first pharyngeal pouch. Named after Bartolomeo Eustachi (1500 - 1574) an Italian anatomist. | |||
'''external auditory meatus''' - (ear canal) develops from the first pharyngeal cleft. | |||
'''ear wax '''- see cerumen. | |||
epithelia - | |||
'''espins''' - calcium-resistant actin-bundling proteins enriched in hair cell stereocilia and sensory cell microvilli and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) | |||
'''eustachian tube''' - (auditory tube) between the middle ear and oral cavity, equalization of pressure in the middle ear. | |||
external auditory canal - | |||
'''fenestra ovalis''' - (oval window) separates the tympanic cavity from the vestibule of the osseous labyrinth. | |||
'''fenestra rotunda''' - (round window) separates the tympanic cavity from the scala tympani of the cochlea. | |||
'''fetus''' - (foetus) term used to describe human development after the 8th week (10th clinical week, LPM) and covers the developmental periods of second and third trimester. | |||
'''fibroblast growth factor 1''' - (Fgf-1) a growth factor released from cochlea sensory epithelium which stimulates spiral ganglion neurite branching. | |||
'''fibroblast growth factor 8''' - (Fgf-8) a growth factor released by inner hair cells which regulates pillar cell number, position and rate of development. | |||
'''fibroblast growth factor receptor 3''' - (Fgfr-3) a tyrosine kinase receptor with a role in the commitment, differentiation and position of pillar cells in the organ of corti | |||
'''fundamental frequency''' - (natural frequency) the lowest frequency in a harmonic series, for the female voice this is about 225 Hz. | |||
'''helicotrema''' - term used to describe the cochlear apex. | |||
Hes - (hairy and enhancer of split) family of factors, which has been shown to be a general negative regulator of neurogenesis {Zheng, 2000 #1936}. | |||
'''hillock''' - a small hill, used to describe the six surface elevations on pharyngeal arch one and two. | |||
Hindbrain - Invaginate - | |||
'''Incus''' - (anvil) auditory ossicle | |||
inner phalangeal cells | |||
'''inner pillar cells''' - organ of Corti cells arranged in rows and form a boundary between the single row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. These cells have surface-associated microtubule bundles. | |||
inner sulcus - area of the cochlear duct | |||
interdental region - | |||
'''internal auditory meatus''' - (internal acoustic meatus, IAM) Anatomical canal in which CN VII and CN VIII ganglia reside and pass through to the brainstem. This bony canal lies between the posterior surface of the petrous pyramid and the bony labyrinth within the dense petrous bone. Also associated clinically with the site where acoustic neuromas may occur. | |||
'''Kolliker's organ''' - (Kollicker's organ, greater epithelial ridge) Developing cochlear structure consisting of columnar-shaped supporting cells filling the inner sulcus and lying directly under the tectorial membrane. This transient organ regresses and generates the space of the inner sulcus. Rudolph Albert von Kolliker (1817-1905)?? | |||
lateral semicircular duct - Limbus - | |||
'''LMP''' - acronym for last menstrual period, used to clinically measure gestation. | |||
'''malleus''' - (hammer) auditory ossicle | |||
'''mastoid process''' - of temporal bone | |||
'''Math1''' - homolog of the Drosophila proneural gene atonal, necessary and sufficient for the production of hair cells in the mouse inner ear. {Chen, 2002 #1932}Negatively regulated by Hes1 and Hes5 | |||
'''meatal plug''' - temporary blockage of the external auditory meatus which forms at the end of the embryonic period and remains present until the seventh month. | |||
'''meatus''' - anatomical opening, cavity or space (external acoustic meatus,internal auditory meatus) | |||
'''Meckel's cartilage''' - first pharyngeal ach cartilage, located within the mandibular prominence. This cartilage first appears at stage 16, stage 20 the beginning of membranous ossification. Named after Johann Friedrich Meckel, (1781 - 1833) a German anatomist. (http://www.whonamedit.com/doctor.cfm/1840.html) | |||
membranous labyrinth - Mesenchyme - Mesoderm - Microtia - Modiolus - | |||
'''mucopolysaccharidosis''' - (MPS IIIB, Sanfilippo Syndrome type B) abnormality caused by a deficiency in the lysosomal enzyme N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (Naglu). Children with MPS IIIB develop abnormal hearing, and mental functioning culminating in early death. | |||
'''netrin-1''' - secreted growth factor, expressed in the organ of Corti and spiral ganglion cells, role in process outgrowth. | |||
neural tube - | |||
'''olivocochlear''' - brainstem cholinergic and GABAergic efferent system that innervates sensory cells and sensory neurons of the inner ear. | |||
organ of Corti - organ of Corti protein II - (OCP-II) cytosolic protein or transcription factor? | |||
'''otolithic membrane''' - extracellular matrix that cover the sensory epithelia of the inner ear. | |||
'''ossicle''' - (small bone) the individual bone of the three middle ear bones (auditory ossicles), which reduce vibrational amplitude but increase force to drive fluid-filled inner ear. | |||
ossify - | |||
otic capsule - | |||
otic cup | |||
otic placode - | |||
otic vesicle - | |||
'''otoconin''' - inner ear biominerals required for vestibular apparatus function. | |||
'''otogelin''' - (Otog) an inner ear specific glycoprotein expressed in cochlea cells at different developmental times. | |||
'''otolithic membrane''' - a membrane within the utricle and saccule containing embedded hair cell cilia and small crystalline bodies of calcium carbonate (otoliths). Functions to detect head motion. | |||
'''otoliths''' - small crystalline bodies of calcium carbonate found within the otolitic membrane of the utricle and saccule. | |||
'''ototoxic''' - compound or drug causing temporary or permanent hearing loss. | |||
'''outer hair cells''' - (OHCs) three rows of hair cells that function to increase basilar membrane motion through a local mechanical feedback process within the cochlea, the "cochlear amplifier". | |||
'''outer pillar cells''' - arranged in rows and form a boundary between the single row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. | |||
'''paratubal musculature''' - muscles lying beside the auditory (Eustachian) tube. The tensor veli, palatini (TVP) and tensor tympani muscles. | |||
perilymph - perilymphatic space - Periotic Capsule - petrous portion - of temporal bone | |||
'''pejvakin gene''' - in humans, two missense mutations in this gene cause nonsyndromic recessive deafness (DFNB59) by affecting the function of auditory neurons. | |||
pharyngeal archpharyngeal pouchpharyngeal membranePharynx | |||
'''pillar cells''' - (PC) form an inner and outer row of support cells that form a boundary between inner and outer hair cells. | |||
''' | |||
Placode | |||
'''preyer reflex''' - ear flick in mouse in response to sound. | |||
presbyacusis | |||
'''prestin''' - a motor protein structurally similar to the anion transporter family expressed in cochlear outer hair cells. | |||
'''preauricular tag''' - skin tags located in front of the external ear opening, are common in neonates and in most cases are normal, though in some cases are indicative of other associated abnormalities. | |||
primordium- | |||
'''protocadherin 15''' - (Pcdh15) required for initial formation of stereocilia bundles and changes in the actin meshwork within hair cells. The Ames waltzer (av) mouse mutant has both auditory and vestibular abnormalities from a mutation in this gene. | |||
'''Reichert's cartilage''' - pharyngeal ach 2 cartilage, named after Karl Bogislaus Reichert (1811 - 1883) a German anatomist. | |||
'''Reissner's membrane''' - (vestibular membrane, vestibular wall) is a membrane located inside the cochlea separating the scala media from scala vestibuli. Named after Ernst Reissner (1824-1878) a German anatomist. “It primarily functions as a diffusion barrier, allowing nutrients to travel from the perilymph to the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth. | |||
rhombomere - | |||
Saccular macula - | |||
Saccule - (Latin, sacculus = a small pouch) | |||
sacculocollic reflex - | |||
scala tympani - one of the three Cochlea cavities, it is filled with perilymph. | |||
'''Scarpa's ganglion''' - (vestibular ganglion) primary afferent vestibular neuron ganglion of the vestibular nerve. Located within the internal auditory meatus. | |||
'''semicircular canals''' - series of fluid-filled loops of the inner ear required for balance and sensing acceleration. | |||
sensorineural - term used to describe one of the two major classes of hearing loss involving the central pathway from the cochlear (other form is conductive loss). | |||
'''space of Nuel''' - within the cochlea, an organ of Corti space between the outer pillar cells and the phalangeal and hair cells. Named after Jean-Pierre Nuel (1847-1920) a Belgian ophthalmologist. | |||
'''spiral ganglion neurons''' - (SGN) innervate the inner (Type I) and outer (Type II) hair cells of the cochlea. | |||
''' | |||
''' | '''stapedius muscle''' - (innervated by CN VII tympanic branch) one of the two muscles in the middle ear, contraction of this muscle pulls the stapes and dampens auditory ossicle movement. | ||
'''stapes''' - (stirrup) a middle ear auditory ossicle (bone).stapes footplate - startle response - | |||
'''stereocilia''' -finger-like projections from the apical surface of sensory hair cells forming the hair bundle in the cochlea. Formed by tightly cross-linked parallel actin filaments in a paracrystalline array with cell surface specializations (tip links, horizontal top connectors, and tectorial membrane attachment crowns). | |||
'''stratified squamous epithelia''' - classification of epithelium which transiently forms a plug in external ear canal to the outer eardrum. | |||
'''stria vascularis''' - forms the outer wall of the cochlear duct of the mammalian cochlea is composed primarily of three types of cells. Marginal cells line the lumen of the cochlear duct and are of epithelial origin. Basal cells also form a continuous layer and they may be mesodermal or derived from the neural crest. Intermediate cells are melanocyte-like cells, presumably derived from the neural crest, and are scattered between the marginal and basal cell layers. The stria forms endolymph and also contains a rich supply of blood vessels. | |||
sulcus - | |||
'''synostotically''' - anatomically normally separate skeletal bones fused together. | |||
'''tectorial membrane''' - extracellular matrix that cover the sensory epithelial hair cells of the organ of corti within the cochlea. | |||
'''alpha-tectorin and beta'''- (TECTA, TECTB) major non-collagenous protein component of the tectorial membrane forming a striated-sheet matrix. Synthesized as glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked, membrane bound precursors. | |||
temporal bone - | |||
'''tensor tympani '''- (innervated by CN V mandibular nerve) one of the two muscles in the middle ear, contraction of this muscle pulls the malleus and tenses the tympanic membrane, dampening auditory ossicle movement. The muscle arises from auditory tube (cartilaginous portion) and is inserted into the malleus (manubrium near the root). | |||
teratogens - trilaminar embryo - | |||
'''tonotopy''' - term describing the mapping along the tectorial membrane within the cochlea of the different sound frequencies. | |||
tympanic cavity - tympanic membrane -Utricle -Vacuolization - Vesicle - vestibular apparatus - vestibular evoked myogenic potential (VEMP) test | |||
'''vestibular ganglion''' - (Scarpa's ganglion) primary afferent vestibular neuron ganglion of the vestibular nerve. Located within the internal auditory meatus. | |||
'''vestibular membrane''' - (Reissner's) extends from the spiral lamina to the outer wall and divides the cochlea into an upper scala vestibuli, a lower scala tympani. | |||
'''Vestibulocochlear Nerve''' - Cranial Nerve VIII | |||
'''Whirlin''' - A PDZ scaffold protein expressed in hair cells at the stereocilia tips, essential for the stereocilia elongation process. The DFNB31 gene mutations cause hearing loss in human and mouse. This protein can interact with membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein, erythrocyte protein p55 (p55). | |||
'''Wnt7a''' - signaling through the Wnt pathway regulates the development of hair cell unidirectional stereociliary bundle orientation. | |||
Latest revision as of 22:34, 23 January 2019
2019
ILI redevelopment.
2016
Removed these images
Original movie media player format
<mediaplayer width='410' height='340' image="http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/images/7/7d/Chicken-neural-crest-migration-01.jpg">File:Chicken-neural crest migration 01.mp4</mediaplayer>
2013
2012
Textbooks
- Before We Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Chapter 20: p460-479
- Essentials of Human Embryology, Larson Chapter 12: p252-272
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology (6th ed.) Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000. Evolution of the mammalian middle ear bones from the reptilian jaw | Chick embryo rhombomere neural crest cells | Some derivatives of the pharyngeal arches | Formation of the Neural Tube | Differentiation of the Neural Tube | Tissue Architecture of the Central Nervous System | Neuronal Types | Snapshot Summary: Central Nervous System and Epidermis
- Neuroscience Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc. ; c2001 The Auditory System | The Inner Ear | The Middle Ear | The External Ear | Early Brain Development | Construction of Neural Circuits | Modification of Brain Circuits as a Result of Experience
- Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th Edn) Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter. New York: Garland Publishing; 2002. Neural Development | The three phases of neural development
- Clinical Methods 63. Cranial Nerves IX and X: The Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves | The Tongue | 126. The Ear and Auditory System | An Overview of the Head and Neck - Ears and Hearing | Audiometry
- Health Services/Technology Assessment Text (HSTAT) Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), 2003 Oct. Developmental Disorders Associated with Failure to Thrive
- Eurekah Bioscience CollectionCranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton
Search
- Bookshelf hearing development
- Pubmed hearing development
Links
- NIDCD - Balance Disorders
Terms
altricial animal - Term used to describe an animal born in a helpless state, with incomplete development of sensory systems at birth. For example rats and mice are born with incomplete development of visual and auditory systems.
ampulla - Term used to describe an anatomical dilation of a tube or canal lumen. Anatomical description of the opening end of the uterine tube lying above the ovary and the enlarged initial segmeny of the semicircular canals of the inner ear vestibular system. (More? [ear6.htm Inner Ear] | [genitalXXuterus.htm Genital System - Female Uterus])
aneurism - (Greek, aneurysma = a widening, aneurysm) A term used to describe an abnormal widening of a vessel or anatomical tubal structure.
aquaeductus vestibuli - see vestibular aqueduct
auditory neuropathy - (AN) abnormality of transmission of sound information to the brain.
auditory tube - (eustachian tube) between the middle ear and oral cavity, has a bony (tympanic 1/3) and cartilaginous (pharyngeal 2/3) portion. The main role is equalization of pressure and fluid drainage in the middle ear.
auricular hillock - see hillock
atresia - narrowing, usually of an anatomical tube or cavity.
autophagocytosis - (Greek, auto = self, phagy = eating, also called autophagy) a cell death mechanism that uses the cell's own lysosomes to self digest.
border cells - columnar cells within the organ of Corti on the medial portion of the basilar membrane.
canalis reuniens - (ductus reuniens, canaliculus reuniens, canalis reuniens, Hensen's canal, Hensen's duct, uniting canal, canalis reuniens of Hensen) short narrow canal connecting the cochlea duct to the saccule. (Victor Hensen, 1835-1924)
cerumen - (ear wax) produced by glands in the skin of the outer portion of the ear canal.
chondrified - the developmental differentiation of cartilage from mesenchye, an embryonic connective tissue.
cristae ampullaris - located in the ampulla of the membranous semicircular canals a region with both supporting and hair cells. The hair cell cilia are embedded in the gelatinous cupula.
claudius cells - (cells of Claudius) columnar cells with microvilli overlying the basilar membrane and extend from Hensen's cells to the spiral prominence. Barrier cells that lie external to the organ of corti in endolymph.
cochlear sac - embryonic structure, which will form the coiled cochlear duct and contribute to the saccule.
cochlear aqueduct - a bony channel containing the fibrous periotic duct. It connects the basal turn of the cochlea perilymphatic space with the subarachnoid space of the posterior cranial cavity.
cochlin - major constituent of the inner ear extracellular matrix.
collagen type II - major constituent of the inner ear extracellular matrix.
conductive loss - term used to describe one of the two major classes of hearing loss involving external and middle ear abnormalities (other form is Sensorineural loss).
connexins - channel proteins of the gap junctions that allow rapid communication between adjacent cells. The two connexins Cx26 and Cx30 are the major proteins of cochlear gap junctions.
connexin 26 - A strikingly high proportion (50%) of congenital bilateral nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness cases have been linked to mutations in the GJB2 coding for the connexin26
cupular deposits - basophilic material on the cupulae of the semicircular ducts, an postnatal ageing phenomenon seen in some vestibular labyrinth.
clinical weeks - taken from last menstrual period (LMP) and therefore approximately two weeks before fertilization occurs.
Deiters' cells
discoidin domain receptor 1 - (DDR1) a tyrosine kinase receptor activated by native collagen, expressed in the basement membrane and with fibrillar collagens. Found in basal cells of the stria vascularis, type III fibrocytes, and cells lining the basilar membrane of the organ of Corti. {Meyer zum Gottesberge, 2008 #1877}
ductus utriculosaccularis -
endochondral ossification - the process of bone formation from a pre-existing cartilage template.
endoderm -
endolymphatic fluid -
endolymphatic sac - inner ear structure that has anatomically both an intraosseous and extraosseous component. Th e sac has functions regulating endolymph that are both secretory and absorptive. Also the site of endolymphatic sac tumors either sporadical occurring or associated with the autosomal-dominant von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease, due to a germ line mutation.
embryological weeks - taken from the time of fertilization which typically occurs around the middle (day 14), or just after, of the typical 28 day menstrual cycle.
Emx2 - homeobox gene affecting middle ear and inner ear development.
eustachian tube - (auditory tube) A cavity linking the pharynx to the middle ear, which develops from the first pharyngeal pouch. Named after Bartolomeo Eustachi (1500 - 1574) an Italian anatomist.
external auditory meatus - (ear canal) develops from the first pharyngeal cleft.
ear wax - see cerumen.
epithelia -
espins - calcium-resistant actin-bundling proteins enriched in hair cell stereocilia and sensory cell microvilli and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs)
eustachian tube - (auditory tube) between the middle ear and oral cavity, equalization of pressure in the middle ear.
external auditory canal -
fenestra ovalis - (oval window) separates the tympanic cavity from the vestibule of the osseous labyrinth.
fenestra rotunda - (round window) separates the tympanic cavity from the scala tympani of the cochlea.
fetus - (foetus) term used to describe human development after the 8th week (10th clinical week, LPM) and covers the developmental periods of second and third trimester.
fibroblast growth factor 1 - (Fgf-1) a growth factor released from cochlea sensory epithelium which stimulates spiral ganglion neurite branching.
fibroblast growth factor 8 - (Fgf-8) a growth factor released by inner hair cells which regulates pillar cell number, position and rate of development.
fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 - (Fgfr-3) a tyrosine kinase receptor with a role in the commitment, differentiation and position of pillar cells in the organ of corti
fundamental frequency - (natural frequency) the lowest frequency in a harmonic series, for the female voice this is about 225 Hz.
helicotrema - term used to describe the cochlear apex.
Hes - (hairy and enhancer of split) family of factors, which has been shown to be a general negative regulator of neurogenesis {Zheng, 2000 #1936}.
hillock - a small hill, used to describe the six surface elevations on pharyngeal arch one and two.
Hindbrain - Invaginate -
Incus - (anvil) auditory ossicle
inner phalangeal cells
inner pillar cells - organ of Corti cells arranged in rows and form a boundary between the single row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. These cells have surface-associated microtubule bundles.
inner sulcus - area of the cochlear duct
interdental region -
internal auditory meatus - (internal acoustic meatus, IAM) Anatomical canal in which CN VII and CN VIII ganglia reside and pass through to the brainstem. This bony canal lies between the posterior surface of the petrous pyramid and the bony labyrinth within the dense petrous bone. Also associated clinically with the site where acoustic neuromas may occur.
Kolliker's organ - (Kollicker's organ, greater epithelial ridge) Developing cochlear structure consisting of columnar-shaped supporting cells filling the inner sulcus and lying directly under the tectorial membrane. This transient organ regresses and generates the space of the inner sulcus. Rudolph Albert von Kolliker (1817-1905)??
lateral semicircular duct - Limbus -
LMP - acronym for last menstrual period, used to clinically measure gestation.
malleus - (hammer) auditory ossicle
mastoid process - of temporal bone
Math1 - homolog of the Drosophila proneural gene atonal, necessary and sufficient for the production of hair cells in the mouse inner ear. {Chen, 2002 #1932}Negatively regulated by Hes1 and Hes5
meatal plug - temporary blockage of the external auditory meatus which forms at the end of the embryonic period and remains present until the seventh month.
meatus - anatomical opening, cavity or space (external acoustic meatus,internal auditory meatus)
Meckel's cartilage - first pharyngeal ach cartilage, located within the mandibular prominence. This cartilage first appears at stage 16, stage 20 the beginning of membranous ossification. Named after Johann Friedrich Meckel, (1781 - 1833) a German anatomist. (http://www.whonamedit.com/doctor.cfm/1840.html)
membranous labyrinth - Mesenchyme - Mesoderm - Microtia - Modiolus -
mucopolysaccharidosis - (MPS IIIB, Sanfilippo Syndrome type B) abnormality caused by a deficiency in the lysosomal enzyme N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (Naglu). Children with MPS IIIB develop abnormal hearing, and mental functioning culminating in early death.
netrin-1 - secreted growth factor, expressed in the organ of Corti and spiral ganglion cells, role in process outgrowth.
neural tube -
olivocochlear - brainstem cholinergic and GABAergic efferent system that innervates sensory cells and sensory neurons of the inner ear.
organ of Corti - organ of Corti protein II - (OCP-II) cytosolic protein or transcription factor?
otolithic membrane - extracellular matrix that cover the sensory epithelia of the inner ear.
ossicle - (small bone) the individual bone of the three middle ear bones (auditory ossicles), which reduce vibrational amplitude but increase force to drive fluid-filled inner ear.
ossify -
otic capsule -
otic cup
otic placode -
otic vesicle -
otoconin - inner ear biominerals required for vestibular apparatus function.
otogelin - (Otog) an inner ear specific glycoprotein expressed in cochlea cells at different developmental times.
otolithic membrane - a membrane within the utricle and saccule containing embedded hair cell cilia and small crystalline bodies of calcium carbonate (otoliths). Functions to detect head motion.
otoliths - small crystalline bodies of calcium carbonate found within the otolitic membrane of the utricle and saccule.
ototoxic - compound or drug causing temporary or permanent hearing loss.
outer hair cells - (OHCs) three rows of hair cells that function to increase basilar membrane motion through a local mechanical feedback process within the cochlea, the "cochlear amplifier".
outer pillar cells - arranged in rows and form a boundary between the single row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells.
paratubal musculature - muscles lying beside the auditory (Eustachian) tube. The tensor veli, palatini (TVP) and tensor tympani muscles.
perilymph - perilymphatic space - Periotic Capsule - petrous portion - of temporal bone
pejvakin gene - in humans, two missense mutations in this gene cause nonsyndromic recessive deafness (DFNB59) by affecting the function of auditory neurons.
pharyngeal archpharyngeal pouchpharyngeal membranePharynx
pillar cells - (PC) form an inner and outer row of support cells that form a boundary between inner and outer hair cells.
Placode
preyer reflex - ear flick in mouse in response to sound.
presbyacusis
prestin - a motor protein structurally similar to the anion transporter family expressed in cochlear outer hair cells.
preauricular tag - skin tags located in front of the external ear opening, are common in neonates and in most cases are normal, though in some cases are indicative of other associated abnormalities.
primordium-
protocadherin 15 - (Pcdh15) required for initial formation of stereocilia bundles and changes in the actin meshwork within hair cells. The Ames waltzer (av) mouse mutant has both auditory and vestibular abnormalities from a mutation in this gene.
Reichert's cartilage - pharyngeal ach 2 cartilage, named after Karl Bogislaus Reichert (1811 - 1883) a German anatomist.
Reissner's membrane - (vestibular membrane, vestibular wall) is a membrane located inside the cochlea separating the scala media from scala vestibuli. Named after Ernst Reissner (1824-1878) a German anatomist. “It primarily functions as a diffusion barrier, allowing nutrients to travel from the perilymph to the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth.
rhombomere -
Saccular macula -
Saccule - (Latin, sacculus = a small pouch)
sacculocollic reflex -
scala tympani - one of the three Cochlea cavities, it is filled with perilymph.
Scarpa's ganglion - (vestibular ganglion) primary afferent vestibular neuron ganglion of the vestibular nerve. Located within the internal auditory meatus.
semicircular canals - series of fluid-filled loops of the inner ear required for balance and sensing acceleration.
sensorineural - term used to describe one of the two major classes of hearing loss involving the central pathway from the cochlear (other form is conductive loss).
space of Nuel - within the cochlea, an organ of Corti space between the outer pillar cells and the phalangeal and hair cells. Named after Jean-Pierre Nuel (1847-1920) a Belgian ophthalmologist.
spiral ganglion neurons - (SGN) innervate the inner (Type I) and outer (Type II) hair cells of the cochlea.
stapedius muscle - (innervated by CN VII tympanic branch) one of the two muscles in the middle ear, contraction of this muscle pulls the stapes and dampens auditory ossicle movement.
stapes - (stirrup) a middle ear auditory ossicle (bone).stapes footplate - startle response -
stereocilia -finger-like projections from the apical surface of sensory hair cells forming the hair bundle in the cochlea. Formed by tightly cross-linked parallel actin filaments in a paracrystalline array with cell surface specializations (tip links, horizontal top connectors, and tectorial membrane attachment crowns).
stratified squamous epithelia - classification of epithelium which transiently forms a plug in external ear canal to the outer eardrum.
stria vascularis - forms the outer wall of the cochlear duct of the mammalian cochlea is composed primarily of three types of cells. Marginal cells line the lumen of the cochlear duct and are of epithelial origin. Basal cells also form a continuous layer and they may be mesodermal or derived from the neural crest. Intermediate cells are melanocyte-like cells, presumably derived from the neural crest, and are scattered between the marginal and basal cell layers. The stria forms endolymph and also contains a rich supply of blood vessels.
sulcus -
synostotically - anatomically normally separate skeletal bones fused together.
tectorial membrane - extracellular matrix that cover the sensory epithelial hair cells of the organ of corti within the cochlea.
alpha-tectorin and beta- (TECTA, TECTB) major non-collagenous protein component of the tectorial membrane forming a striated-sheet matrix. Synthesized as glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked, membrane bound precursors.
temporal bone -
tensor tympani - (innervated by CN V mandibular nerve) one of the two muscles in the middle ear, contraction of this muscle pulls the malleus and tenses the tympanic membrane, dampening auditory ossicle movement. The muscle arises from auditory tube (cartilaginous portion) and is inserted into the malleus (manubrium near the root).
teratogens - trilaminar embryo -
tonotopy - term describing the mapping along the tectorial membrane within the cochlea of the different sound frequencies.
tympanic cavity - tympanic membrane -Utricle -Vacuolization - Vesicle - vestibular apparatus - vestibular evoked myogenic potential (VEMP) test
vestibular ganglion - (Scarpa's ganglion) primary afferent vestibular neuron ganglion of the vestibular nerve. Located within the internal auditory meatus.
vestibular membrane - (Reissner's) extends from the spiral lamina to the outer wall and divides the cochlea into an upper scala vestibuli, a lower scala tympani.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve - Cranial Nerve VIII
Whirlin - A PDZ scaffold protein expressed in hair cells at the stereocilia tips, essential for the stereocilia elongation process. The DFNB31 gene mutations cause hearing loss in human and mouse. This protein can interact with membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein, erythrocyte protein p55 (p55).
Wnt7a - signaling through the Wnt pathway regulates the development of hair cell unidirectional stereociliary bundle orientation.