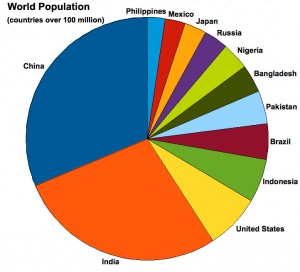
India Statistics
| Embryology - 23 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
This page links to the current online resources available to explore Indian population and birth data.
| Statistics Links: Introduction | Reports | World Population | World Fertility | World Infant Mortality | Maternal Mortality | Australia | Brazil | Canada | China | Germany | India | Indonesia | Europe | Myanmar | Netherlands | Spain | United Kingdom | Romania | Uganda | United States | BGD Tutorial - Applied Embryology and Teratology | National Perinatal Statistics Unit | AIHW | Category:Statistics | |
|
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: India Embryology <pubmed limit=5>India Embryology</pubmed> |
Birth Weight and Nutrition
- 28% of infants with low birthweight, 2005-2009
- 41% Early initiation of breastfeeding, 2005-2009
- 46% of children (2005-2009) who are: exclusively breastfed (<6 months)
- 57% of children (2005-2009) who are: breastfed with complementary food (6-9 months)
- 77% of children (2005-2009) who are: still breastfeeding (20-23 months)
- 48% of under-fives (2003 -2009) suffering from: underweight (NCHS/WHO), moderate & severe
- 43% of under-fives (2003 -2009) suffering from: underweight (WHO), moderate & severe
- 16% of under-fives (2003 -2009) suffering from: underweight (WHO), severe
- 20% of under-fives (2003 -2009) suffering from: wasting (WHO), moderate & severe
- 48% of under-fives (2003 -2009) suffering from: stunting (WHO), moderate & severe
- 66% Full coverage (2009) Vitamin A supplementation coverage rate (6-59 months)
- 51% of households consuming iodized salt, 2003-2009
- Data: Unicef 2011
Abnormal Development
- approximately half a million children are born annually with congenital malformations[4]
- most of which are related to genetic or chromosomal aberration
- estimated 9,000 babies with thalassaemia major
- estimated 5,200 babies with sickle cell disease
- estimated 21,000 babies with Down syndrome
Cleft Lip and Palate
A study was conducted in 2001 in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India, with a population of 76 million.[5]
- birth rate of clefts was found to be 1.09 for every 1000 live births.
- 65% of the children born with clefts were males.
- type of cleft showed 33% had CL, 64% had CLP, 2% had CP and 1% had rare craniofacial clefts
- Unilateral cleft lips were found in 79% of the patients.
- Of the unilateral cleft lips 64% were left sided.
- birth rate of clefts was found to be
- comparable with other Asian studies
- lower than found in other studies in Caucasian populations
- higher than in African populations.
See also the 2010 review "A status report on management of cleft lip and palate in India".[6]
General Statistics
Population 1,189,172,906 (July 2011 est.) country comparison to the world: 2
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 29.7% (male 187,450,635/female 165,415,758)
- 15-64 years: 64.9% (male 398,757,331/female 372,719,379)
- 65 years and over: 5.5% (male 30,831,190/female 33,998,613) (2011 est.)
Median age
- total: 26.2 years
- male: 25.6 years
- female: 26.9 years (2011 est.)
Population growth rate
- 1.344% (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 86
Birth rate
- 20.97 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 84
Death rate
- 7.48 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 117
Sex ratio
- at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.13 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.91 male(s)/female
- total population: 1.08 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- total: 47.57 deaths/1,000 live births
- country comparison to the world: 51
- male: 46.18 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 49.14 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 66.8 years
- country comparison to the world: 161
- male: 65.77 years
- female: 67.95 years (2011 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 2.62 children born/woman (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 79
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 29.7% (male 187,450,635/female 165,415,758)
- 15-64 years: 64.9% (male 398,757,331/female 372,719,379)
- 65 years and over: 5.5% (male 30,831,190/female 33,998,613) (2011 est.)
Median age
- total: 26.2 years
- male: 25.6 years
- female: 26.9 years (2011 est.)
Population growth rate
- 1.344% (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 86
Birth rate
- 20.97 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 84
Death rate
- 7.48 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 117
Sex ratio
- at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.13 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.91 male(s)/female
- total population: 1.08 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- total: 47.57 deaths/1,000 live births
- country comparison to the world: 51
- male: 46.18 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 49.14 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 66.8 years
- country comparison to the world: 161
- male: 65.77 years
- female: 67.95 years (2011 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 2.62 children born/woman (2011 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 79
HIV/AIDS
- 2.4 million (2009 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 4
HIV/AIDS - deaths
- 170,000 (2009 est.)
- country comparison to the world: 3
Major infectious diseases
- degree of risk: high
- food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
- vectorborne diseases: chikungunya, dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
- animal contact disease: rabies
- water contact disease: leptospirosis
- highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country
Ethnic groups
- Data: The World Factbook India
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- Indian Government Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation | Statistics
- UNICEF Indian Statistics
- The World Factbook India
- Global Polio Eradication India
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 23) Embryology India Statistics. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/India_Statistics
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ <pubmed>24277966</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>21918640</pubmed>| PLoS Med.
- ↑ Manchanda S, Saikia B, Gupta N, Chowdhary S, Puliyel JM. Sex ratio at birth in India, its relation to birth order, sex of previous children and use of indigenous medicine. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20097. PMID21697990
- ↑ WHO - Oladapo OT. Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis: RHL commentary (last revised: 1 April 2009). The WHO Reproductive Health Library; Geneva: World Health Organization.
- ↑ <pubmed>21217978</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>20924454</pubmed>