File:Trisomy 21 newborn.jpg
From Embryology
Trisomy_21_newborn.jpg (320 × 240 pixels, file size: 16 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
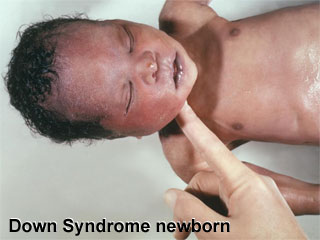
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Newborn
Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children.
The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 in 650 to 1,000 live births, in Australia between 1991-97 there were 2,358 Trisomy 21 (Down) infants.
- The normal human karyotypes contain 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes.
- The karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement as identified by staining and can only be identified during cell division when chromosomes are folded.
- The chromosomes when organised as an image in sequence are called a karyogram or idiogram.
- Links: Trisomy 21
Image Source: CDC Dr. Godfrey P. Oakley
UNSW Embryology http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Defect/page21.htm
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:37, 5 August 2009 |  | 320 × 240 (16 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Newborn Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisom |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: