2011 Lab 10: Difference between revisions
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{2011Lab10}} | |||
==Introduction== | |||
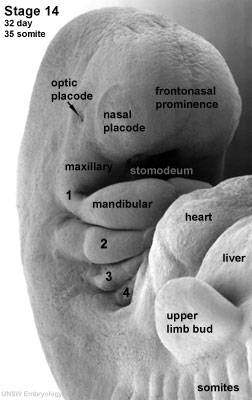
[[File:Stage14 sem2cl.jpg|thumb|Human embryo sensory placodes ([[Week 5]], [[Carnegie stage 14|stage 14]])]] | |||
This practical will introduce the development of the special sensory structures associated with hearing, vision, smell and taste. This topic is closely related to neural development through the fetal and postnatal periods. | |||
== | |||
[[File: | |||
[[ | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | | [[File:Hearing cartoon.jpg|160px|link=Sensory_-_Hearing_and_Balance_Development]] | ||
| | | [[File:Stage_22_image_153.jpg|160px|link=Sensory_-_Vision_Development]] | ||
| | | [[File:Stage_22_image_209.jpg|160px|link=Sensory_-_Smell_Development]] | ||
| | | [[File:Tongue_-_taste_cartoon.jpg|160px|link=Sensory - Taste Development]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <center>[[Sensory_-_Hearing_and_Balance_Development|Hearing Development]]</center> | ||
| <center>[[Sensory_-_Vision_Development|Vision Development]]</center> | |||
| [[ | | <center>[[Sensory_-_Smell_Development|Smell Development]]</center> | ||
| <center>[[Sensory - Taste Development|Taste Development]]</center> | |||
| [[ | |||
| [[ | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
== | ==Textbooks== | ||
{| | |||
| [[File:The Developing Human, 8th edn.jpg|80px]] | |||
| Moore, K.L. & Persuad, T.V.N. (2008). <i>The Developing Human: clinically oriented embryology</i> (8<sup>th</sup> ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. | |||
The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection and can also be accessed through this [http://searchfirst.library.unsw.edu.au/primo_library/libweb/action/search.do?vid=UNSW&fn=search&vl(freeText0)=UNSW_SFX14190000000048007 UNSW Library connection]. | |||
* | * [http://www.mdconsult.com/books/linkTo?type=bookPage&isbn=978-1-4160-3706-4&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-3706-4..50012-8 Chapter 9 - The Pharyngeal Apparatus] | ||
* | * [http://www.mdconsult.com/books/linkTo?type=bookPage&isbn=978-1-4160-3706-4&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-3706-4..50021-9 Chapter 18 - The Eye and Ear] | ||
|- | |||
| [[File:Larsen's human embryology 4th edn.jpg|80px]] | |||
| Schoenwolf, G.C., Bleyl, S.B., Brauer, P.R. and Francis-West, P.H. (2009). <i>Larsen’s Human Embryology</i> (4<sup>th</sup> ed.). New York; Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. | |||
: | The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection and can also be accessed through this [http://searchfirst.library.unsw.edu.au/primo_library/libweb/action/search.do?vid=UNSW&fn=search&vl(freeText0)=UNSW_SFX14190000000047996 UNSW Library connection]. | ||
* [http://www.mdconsult.com/books/linkTo?type=bookPage&isbn=978-0-443-06811-9&eid=4-u1.0-B978-0-443-06811-9..10016-8 Chapter 16 - Development of the Pharyngeal Apparatus and Face] | |||
* [http://www.mdconsult.com/books/linkTo?type=bookPage&isbn=978-0-443-06811-9&eid=4-u1.0-B978-0-443-06811-9..10017-X Chapter 17 - Development of the Ears and Eye] | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Logo.png|80px]] | |||
| Hill, M.A. (2011) <i>UNSW Embryology</i> (11<sup>th</sup> ed.). Sydney:UNSW. | |||
* [[Media:BGDB PracManual 2011 Practical 6.pdf|BGDB Practical Manual 2011 Practical 6]] | |||
* {{Template:Senses Links}} | |||
|} | |||
{{2011Lab10}} | |||
{{2011ANAT2341}} | {{2011ANAT2341}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:27, 5 October 2011
| 2011 Lab 10: Introduction | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Introduction
This practical will introduce the development of the special sensory structures associated with hearing, vision, smell and taste. This topic is closely related to neural development through the fetal and postnatal periods.
|
|
|
|
Textbooks

|
Moore, K.L. & Persuad, T.V.N. (2008). The Developing Human: clinically oriented embryology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders.
The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection and can also be accessed through this UNSW Library connection. | |

|
Schoenwolf, G.C., Bleyl, S.B., Brauer, P.R. and Francis-West, P.H. (2009). Larsen’s Human Embryology (4th ed.). New York; Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
The following chapter links only work with a UNSW connection and can also be accessed through this UNSW Library connection. | |

|
Hill, M.A. (2011) UNSW Embryology (11th ed.). Sydney:UNSW.
|
| 2011 Lab 10: Introduction | Early Embryo | Late Embryo | Fetal | Postnatal | Abnormalities | Online Assessment |
Co-ordinator Note
Dr Mark Hill |
ANAT2341 Embryology S2 2011
|
Course Content 2011
2011 Timetable: | Embryology Introduction | Fertilization | Cell Division/Fertilization | Week 1 and 2 Development | Week 3 Development | Week 1 to 3 | Mesoderm Development | Ectoderm, Early Neural, Neural Crest | Trilaminar Embryo to Early Embryo | Early Vascular Development | Placenta | Vascular and Placenta | Endoderm, Early Gastrointestinal | Respiratory Development | Endoderm and Respiratory | Head Development | Neural Crest Development | Head and Neural Crest | Musculoskeletal Development | Limb Development | Musculoskeletal | Renal Development | Genital | Kidney and Genital | Sensory | Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Endocrine Development | Endocrine | Heart | Integumentary Development | Heart and Integumentary | Fetal | Birth and Revision | Fetal
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 19) Embryology 2011 Lab 10. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/2011_Lab_10
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G