File:Skull CT normal sutures 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Skull Normal Sutures== Computed Tomography (CT) scan with 3D surface-rendered reconstructions. ===A - Vertex view=== ===B - Lateral view=== * (a) Metopic suture; (b) coronal sutures; (c) sagittal suture; (d) lambdoid suture; (e) squamosal suture; (f) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Skull Normal Sutures== | ==Skull Normal Sutures== | ||
Computed Tomography (CT) scan with 3D surface-rendered reconstructions. | Computed Tomography (CT) scan with 3D surface-rendered reconstructions. Vertex and Lateral view. | ||
=== | ===Sutures and Fontanels=== | ||
* '''a''' - Metopic suture | |||
* | * '''b''' - coronal sutures | ||
* '''c''' - sagittal suture | |||
* '''d''' - lambdoid suture | |||
* '''e''' - squamosal suture | |||
* '''f''' - anterior fontanel | |||
* '''g''' - posterior fontanel | |||
* '''h''' - sphenoidal fontanel | |||
* '''i''' - mastoid fontanel | |||
{{Skull_CT_links}} | |||
See also [[:File:Skull CT normal sutures 01.jpg|Vertex view 2]] | |||
===Lateral view=== | |||
=== | |||
* Cranial vault bones usually ossify from the center to periphery, which results in this “widened” appearance of the sutures in the newborn. | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Musculoskeletal_System_-_Skull_Development|Skull Development]] | [[Book_-_Contributions_to_Embryology_Carnegie_Institution_No.48#The_skull_of_a_human_fetus_of_43_millimeters_greatest_length|Historic - skull of a human fetus of 43 millimeters greatest length]] | [[Computed Tomography]] | :'''Links:''' [[Musculoskeletal_System_-_Skull_Development|Skull Development]] | [[Book_-_Contributions_to_Embryology_Carnegie_Institution_No.48#The_skull_of_a_human_fetus_of_43_millimeters_greatest_length|Historic - skull of a human fetus of 43 millimeters greatest length]] | [[Computed Tomography]] | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:21431034}} | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
Paritosh C Khanna © 2007 - 2012 Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging | |||
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported ([http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ CC BY-NC-SA 3.0]) | This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported ([http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ CC BY-NC-SA 3.0]) | ||
Original file name: Figure 1(A-E): IJRI-21-49-g001.jpg | Original file name: Figure 1(A-E): IJRI-21-49-g001.jpg http://www.ijri.org/viewimage.asp?img=IndianJRadiolImaging_2011_21_1_49_76055_f2.jpg resized and relabelled. | ||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Human]] [[Category:Skull]] [[Category:Computed Tomography]] | [[Category:Human]] [[Category:Skull]] [[Category:Computed Tomography]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:13, 21 March 2018
Skull Normal Sutures
Computed Tomography (CT) scan with 3D surface-rendered reconstructions. Vertex and Lateral view.
Sutures and Fontanels
- a - Metopic suture
- b - coronal sutures
- c - sagittal suture
- d - lambdoid suture
- e - squamosal suture
- f - anterior fontanel
- g - posterior fontanel
- h - sphenoidal fontanel
- i - mastoid fontanel
- Skull CT Images: Normal overview | Normal vertex and lateral | Normal endocranial and vertex | Normal Vertex - Fontanels | Dolichocephaly and Scaphocephaly | Coronal Synostosis | Anterior Plagiocephaly | Turricephaly | Posterior Plagiocephaly | Deformational Plagiocepahly | Trigonocephaly | Oxycephaly | Computed Tomography
See also Vertex view 2
Lateral view
- Cranial vault bones usually ossify from the center to periphery, which results in this “widened” appearance of the sutures in the newborn.
- Links: Skull Development | Historic - skull of a human fetus of 43 millimeters greatest length | Computed Tomography
Reference
Khanna PC, Thapa MM, Iyer RS & Prasad SS. (2011). Pictorial essay: The many faces of craniosynostosis. Indian J Radiol Imaging , 21, 49-56. PMID: 21431034 DOI.
Copyright
Paritosh C Khanna © 2007 - 2012 Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
Original file name: Figure 1(A-E): IJRI-21-49-g001.jpg http://www.ijri.org/viewimage.asp?img=IndianJRadiolImaging_2011_21_1_49_76055_f2.jpg resized and relabelled.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 3) Embryology Skull CT normal sutures 01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Skull_CT_normal_sutures_01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 08:23, 17 March 2012 | 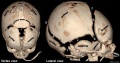 | 1,000 × 526 (89 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Skull Normal Sutures== Computed Tomography (CT) scan with 3D surface-rendered reconstructions. ===A - Vertex view=== ===B - Lateral view=== * (a) Metopic suture; (b) coronal sutures; (c) sagittal suture; (d) lambdoid suture; (e) squamosal suture; (f |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 5 pages use this file: