File:Integumentary touch dome functions.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(Z8600021 uploaded a new version of File:Integumentary touch dome functions.jpg) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. | Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. | ||
===Reference=== | |||
<pubmed>24862916</pubmed> | |||
PMID 24862916 PMCID: PMC4180785 DOI: 10.1111/exd.12456 | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. | Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. | ||
{{Footer}} | |||
Revision as of 10:03, 22 September 2016
Merkel cells and touch domes: more than mechanosensory functions? Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16.
Reference
<pubmed>24862916</pubmed>
PMID 24862916 PMCID: PMC4180785 DOI: 10.1111/exd.12456
Copyright
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 2) Embryology Integumentary touch dome functions.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Integumentary_touch_dome_functions.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:02, 22 September 2016 | 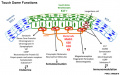 | 893 × 556 (97 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 10:02, 22 September 2016 |  | 950 × 664 (115 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | Merkel cells and touch domes: more than mechanosensory functions? Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. ==Integumentary touch dome functions== Xiao Y1, Williams JS, Brownell I. Abstract The touch dome (TD) i... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: